Apache ShardingSphere 是一套开源的分布式数据库中间件解决方案组成的生态圈,它由 JDBC、Proxy 和 Sidecar(规划中)这 3 款相互独立,却又能够混合部署配合使用的产品组成。 它们均提供标准化的数据分片、分布式事务和数据库治理功能,可适用于如 Java 同构、异构语言、云原生等各种多样化的应用场景。
ShardingSphere 已于2020年4月16日成为 Apache 软件基金会的顶级项目。
分布式系统CAP理论
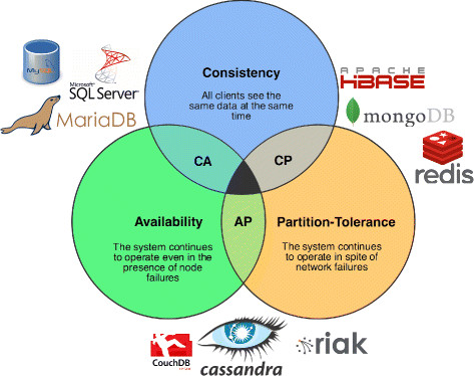
一致性(Consistency)
一致性指
all nodes see the same data at the same time,即更新操作成功并返回客户端完成后,所有节点在同一时间的数据完全一致,不能存在中间状态。关于一致性,如果用户时刻看到的数据都是一致的,那么称之为强一致性。如果允许存在中间状态,只要求经过一段时间后,数据最终是一致的,则称之为最终一致性。此外,如果允许存在部分数据不一致,那么就称之为弱一致性
可用性(Availability)
可用性是指系统提供的服务必须一直处于可用的状态,对于用户的每一个操作请求总是能够在有限的时间内返回结果。
有限的时间内是指:对于用户的一个操作请求,系统必须能够在指定的时间内返回对应的处理结果,如果超过了这个时间范围,那么系统就被认为是不可用的。返回结果是可用性的另一个非常重要的指标,它要求系统在完成对用户请求的处理后,返回一个正常的响应结果,不论这个结果是成功还是失败。
分区容错性(Partition tolerance )
布式系统在遇到任何网络分区故障的时候,仍然需要能够保证对外提供满足一致性和可用性的服务,除非是整个网络环境都发生了故障。
X/Open DTP模型与XA规范
X/Open,即现在的open group,是一个独立的组织,主要负责制定各种行业技术标准。官网地址:http://www.opengroup.org/。X/Open组织主要由各大知名公司或者厂商进行支持,这些组织不光遵循X/Open组织定义的行业技术标准,也参与到标准的制定。下图展示了open group目前主要成员(官网截图):

DTP模型
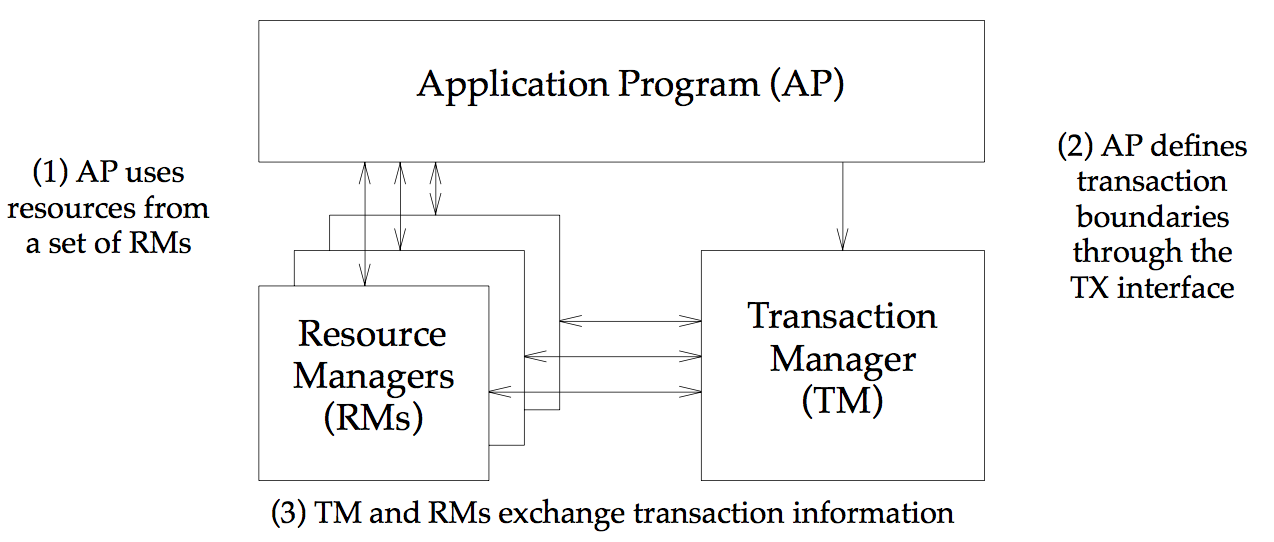
应用程序(Application Program ,简称AP):用于定义事务边界(即定义事务的开始和结束),并且在事务边界内对资源进行操作。
资源管理器(Resource Manager,简称RM,一般也称为事务参与者):如数据库、文件系统等,并提供访问资源的方式。
事务管理器(Transaction Manager ,简称TM,一般也称为事务协调者):负责分配事务唯一标识,监控事务的执行进度,并负责事务的提交、回滚等。
XA规范
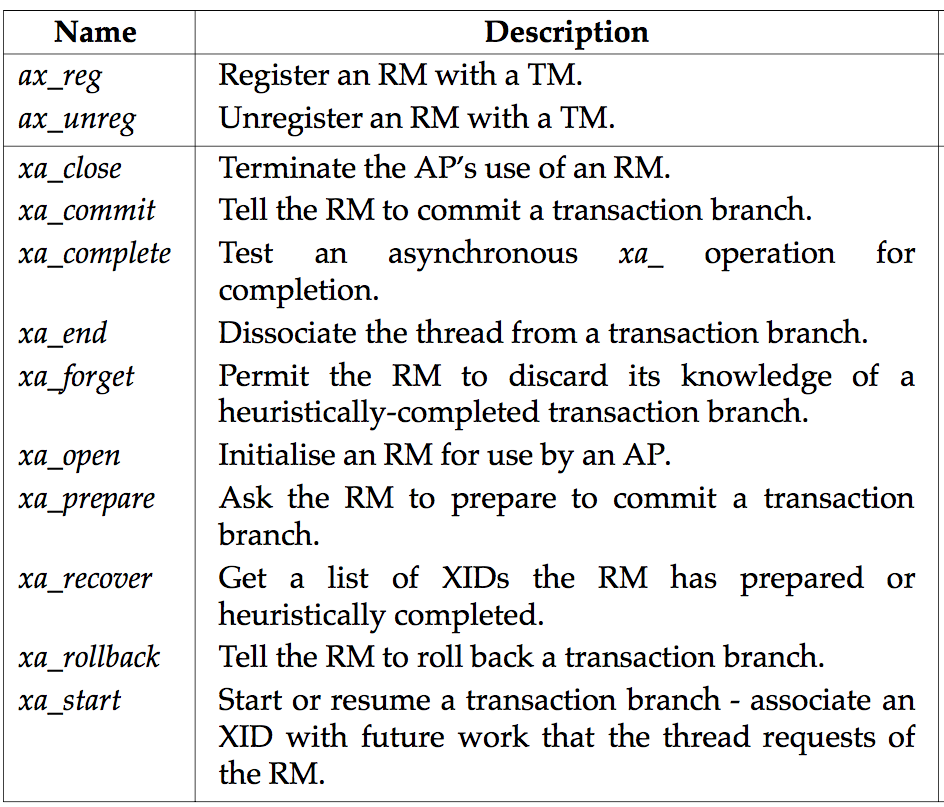
这里的接口规范特别多,我们只要来讲讲几个最重要的。
xa_start: 在RM端调用此接口开启一个XA事务,后面需要接上XID作为参数。xa_end: 取消当前线程与事务的关联, 与xa_start是配对使用。xa_prepare: 询问RM是否已经准备好了提交事务。xa_commit: 通知RM提交事务分支。xa_rollback: 通知RM提交回滚事务分支。
XA二阶段提交
阶段一:TM通知各个RM准备提交它们的事务分支。如果RM判断自己进行的工作可以被提交,那就就对工作内容进行持久化,再给TM肯定答复;要是发生了其他情况,那给TM的都是否定答复。在发送了否定答复并回滚了已经的工作后,RM就可以丢弃这个事务分支信息。阶段二:TM根据阶段1各个RM prepare的结果,决定是提交还是回滚事务。如果所有的RM都prepare成功,那么TM通知所有的RM进行提交;如果有RM prepare失败的话,则TM通知所有RM回滚自己的事务分支。
MySQL对XA协议的支持
MySQL 从5.0.3开始支持XA分布式事务,且只有InnoDB存储引擎支持XA事务。 MySQL 在DTP模型中也是属于资源管理器RM。
MySQL XA 事务的 SQL语法
XA START xid //开启XA事务,xid是一个唯一值,表示事务分支标识符 XA END xid //结束一个XA事务, XA PREPARE xid 准备提交 XA COMMIT xid [ONE PHASE] //提交事务。两阶段提交协议中,如果只有一个RM参与,那么可以优化为一阶段提交 XA ROLLBACK xid //回滚 XA RECOVER [CONVERT XID] //列出所有处于PREPARE阶段的XA事务
MySQL xid详解
mysql中使用xid来作为一个事务分支的标识符。通过C语言进行描述,如下:
/∗∗ Transaction branch identification: XID and NULLXID:∗/#define XIDDATASIZE 128 /∗ size in bytes ∗/#define MAXGTRIDSIZE 64 /∗ maximum size in bytes of gtrid ∗/#define MAXBQUALSIZE 64 /∗ maximum size in bytes of bqual ∗/struct xid_t {
long formatID; /* format identifier */
long gtrid_length; /* value 1-64 */
long bqual_length; /* value 1-64 */
char data[XIDDATASIZE];
};/∗∗ A value of -1 in formatID means that the XID is null.∗/typedef struct xid_t XID;/∗∗ Declarations of routines by which RMs call TMs:∗/extern int ax_reg(int, XID ∗, long);extern int ax_unreg(int, long);gtrid:全局事务标识符(global transaction identifier),最大不能超过64字节。bqual:分支限定符(branch qualifier),最大不能超过64字节。formatId:记录gtrid、bqual的格式,类似于memcached中flags字段的作用。data:xid的值,其是 gtrid和bqual拼接后的内容。。
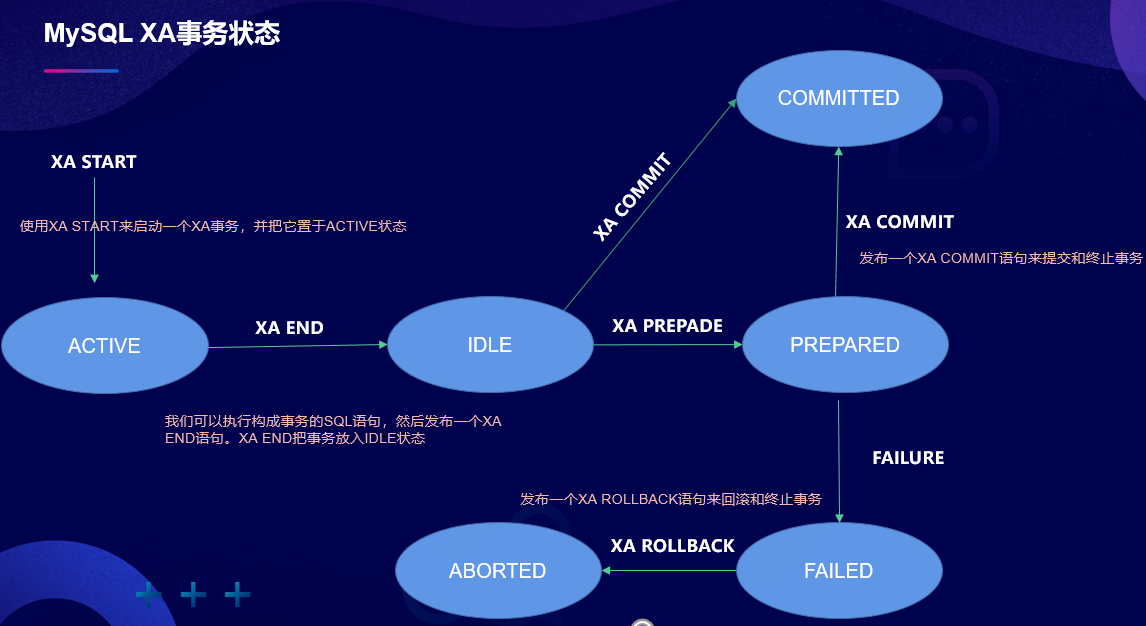
MySQL XA事务状态
JTA规范
JTA(Java Transaction API):为J2EE平台提供了分布式事务服务(distributed transaction)的能力。 某种程度上,可以认为JTA规范是XA规范的Java版,其把XA规范中规定的DTP模型交互接口抽象成Java接口中的方法,并规定每个方法要实现什么样的功能。
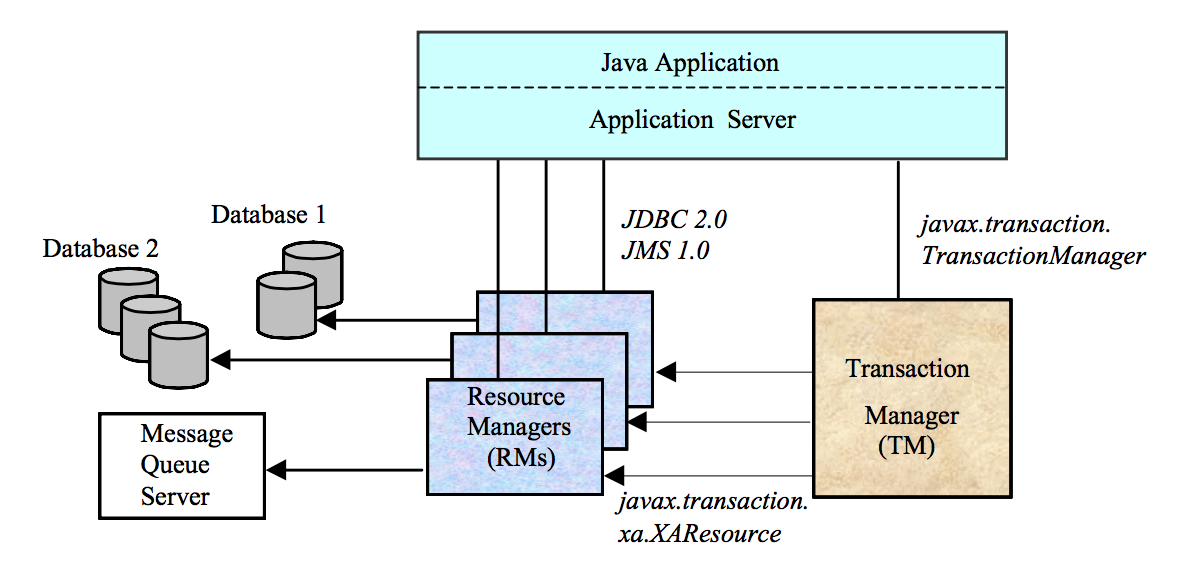
JTA 定义的接口
javax.transaction.TransactionManager: 事务管理器,负责事务的begin,commit,rollback等命令。javax.transaction.UserTransaction:用于声明一个分布式事务。javax.transaction.TransactionSynchronizationRegistry:事务同步注册javax.transaction.xa.XAResource:定义RM提供给TM操作的接口javax.transaction.xa.Xid:事务xid接口。
TM provider:
实现UserTransaction、TransactionManager、Transaction、TransactionSynchronizationRegistry、Synchronization、Xid接口,通过与XAResource接口交互来实现分布式事务。
RM provider:
XAResource接口需要由资源管理器者来实现,XAResource接口中定义了一些方法,这些方法将会被TM进行调用,如:
start方法:开启事务分支
end方法:结束事务分支
prepare方法:准备提交
commit方法:提交
rollback方法:回滚
recover方法:列出所有处于PREPARED状态的事务分支
ShardingSphere对XA分布式事务的支持
ShardingSphere针对XA分布式事务的接口以及JTA规范,提供了标准的,基于SPI实现的org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.spi.ShardingTransactionManager。
public interface ShardingTransactionManager extends AutoCloseable {
/** * Initialize sharding transaction manager. * * @param databaseType database type * @param resourceDataSources resource data sources */
void init(DatabaseType databaseType, Collection<ResourceDataSource> resourceDataSources);
/** * Get transaction type. * * @return transaction type */
TransactionType getTransactionType();
/** * Judge is in transaction or not. * * @return in transaction or not */
boolean isInTransaction();
/** * Get transactional connection. * * @param dataSourceName data source name * @return connection * @throws SQLException SQL exception */
Connection getConnection(String dataSourceName) throws SQLException;
/** * Begin transaction. */
void begin();
/** * Commit transaction. */
void commit();
/** * Rollback transaction. */
void rollback();}对于XA分布式事务的支持的具体实现类为 :org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.xa.XAShardingTransactionManager。 在此类中,会调用基于SPI实现的org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.xa.spi.XATransactionManager,来进行XA事务的管理操作。
总结
我们了解了分布式事务的CAP理论,了解了X/Open的DTP模型,以及XA的接口规范,MySQL对XA协议的支持。最好我们讲解了JTA的规范,以及ShardingSphere对XA事务进行整合的时候定义的SPI接口,这些都是很重要的理论基础,接下来,我们将详细来讲解基于AtomkikosXATransactionManager的具体实现,以及源码解析。
Shardingsphere整合Atomikos对XA分布式事务的源码解析
Atomikos(https://www.atomikos.com/),其实是一家公司的名字,提供了基于JTA规范的XA分布式事务TM的实现。其旗下最著名的产品就是事务管理器。产品分两个版本:
TransactionEssentials:开源的免费产品;
ExtremeTransactions:上商业版,需要收费。
这两个产品的关系如下图所示:
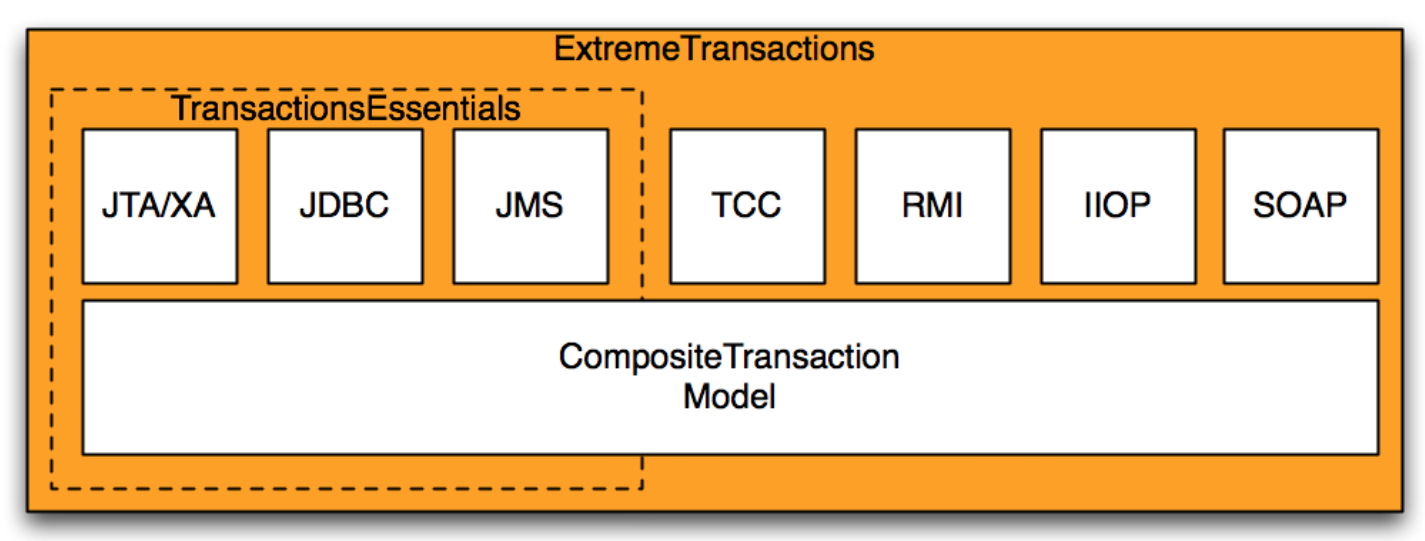
ExtremeTransactions在TransactionEssentials的基础上额外提供了以下功能(重要的):
支持TCC:这是一种柔性事务
支持通过RMI、IIOP、SOAP这些远程过程调用技术,进行事务传播。
事务日志云存储,云端对事务进行恢复,并且提供了完善的管理后台。
org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.xa.XAShardingTransactionManager详解
我们简单的来回顾下org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.spi.ShardingTransactionManager
public interface ShardingTransactionManager extends AutoCloseable {
/** * Initialize sharding transaction manager. * * @param databaseType database type * @param resourceDataSources resource data sources */
void init(DatabaseType databaseType, Collection<ResourceDataSource> resourceDataSources);
/** * Get transaction type. * * @return transaction type */
TransactionType getTransactionType();
/** * Judge is in transaction or not. * * @return in transaction or not */
boolean isInTransaction();
/** * Get transactional connection. * * @param dataSourceName data source name * @return connection * @throws SQLException SQL exception */
Connection getConnection(String dataSourceName) throws SQLException;
/** * Begin transaction. */
void begin();
/** * Commit transaction. */
void commit();
/** * Rollback transaction. */
void rollback();}我们重点县关注init方法,从它的命名,你就应该能够看出来,这是整个框架的初始化方法,让我们来看看它是如何进行初始化的。
private final Map<String, XATransactionDataSource> cachedDataSources = new HashMap<>();
private final XATransactionManager xaTransactionManager = XATransactionManagerLoader.getInstance().getTransactionManager();
@Override
public void init(final DatabaseType databaseType, final Collection<ResourceDataSource> resourceDataSources) {
for (ResourceDataSource each : resourceDataSources) {
cachedDataSources.put(each.getOriginalName(), new XATransactionDataSource(databaseType, each.getUniqueResourceName(), each.getDataSource(), xaTransactionManager));
}
xaTransactionManager.init();
}首先SPI的方式加载XATransactionManager的具体实现类,这里返回的就是
org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.xa.atomikos.manager.AtomikosTransactionManager。我们在关注下
new XATransactionDataSource(), 进入org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.xa.jta.datasource。XATransactionDataSource类的构造方法。
public XATransactionDataSource(final DatabaseType databaseType, final String resourceName, final DataSource dataSource, final XATransactionManager xaTransactionManager) {
this.databaseType = databaseType;
this.resourceName = resourceName;
this.dataSource = dataSource;
if (!CONTAINER_DATASOURCE_NAMES.contains(dataSource.getClass().getSimpleName())) {
// 重点关注 1 ,返回了xaDatasource xaDataSource = XADataSourceFactory.build(databaseType, dataSource);
this.xaTransactionManager = xaTransactionManager;
// 重点关注2 注册资源 xaTransactionManager.registerRecoveryResource(resourceName, xaDataSource);
}
}我们重点来关注
XADataSourceFactory.build(databaseType, dataSource),从名字我们就可以看出,这应该是返回JTA规范里面的XADataSource,在ShardingSphere里面很多的功能,可以从代码风格的命名上就能猜出来,这就是优雅代码(吹一波)。不多逼逼,我们进入该方法。
public final class XADataSourceFactory {
public static XADataSource build(final DatabaseType databaseType, final DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceSwapper(XADataSourceDefinitionFactory.getXADataSourceDefinition(databaseType)).swap(dataSource);
}}首先又是一个SPI定义的
XADataSourceDefinitionFactory,它根据不同的数据库类型,来加载不同的方言。然后我们进入swap方法。
public XADataSource swap(final DataSource dataSource) {
XADataSource result = createXADataSource();
setProperties(result, getDatabaseAccessConfiguration(dataSource));
return result;
}很简明,第一步创建,
XADataSource,第二步给它设置属性(包含数据的连接,用户名密码等),然后返回。返回
XATransactionDataSource类,关注xaTransactionManager.registerRecoveryResource(resourceName, xaDataSource);从名字可以看出,这是注册事务恢复资源。这个我们在事务恢复的时候详解。返回
XAShardingTransactionManager.init(),我们重点来关注:xaTransactionManager.init();,最后进入AtomikosTransactionManager.init()。流程图如下:
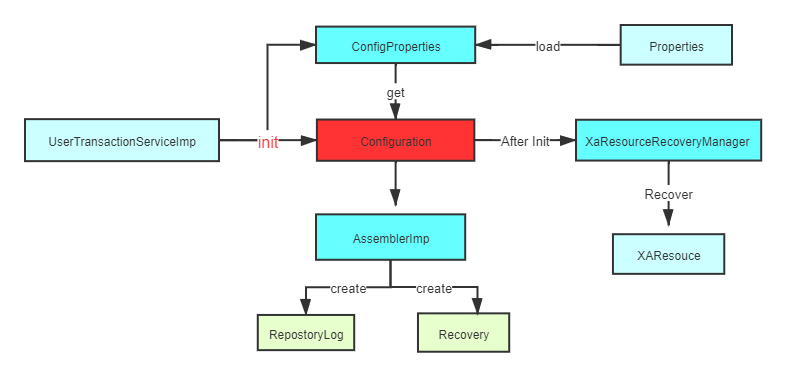
代码:
public final class AtomikosTransactionManager implements XATransactionManager {
private final UserTransactionManager transactionManager = new UserTransactionManager();
private final UserTransactionService userTransactionService = new UserTransactionServiceImp();
@Override
public void init() {
userTransactionService.init();
}}进入
UserTransactionServiceImp.init()
private void initialize() {
//添加恢复资源 不用关心 for (RecoverableResource resource : resources_) {
Configuration.addResource ( resource );
}
for (LogAdministrator logAdministrator : logAdministrators_) {
Configuration.addLogAdministrator ( logAdministrator );
}
//注册插件 不用关心 for (TransactionServicePlugin nxt : tsListeners_) {
Configuration.registerTransactionServicePlugin ( nxt );
}
//获取配置属性 重点关心 ConfigProperties configProps = Configuration.getConfigProperties();
configProps.applyUserSpecificProperties(properties_);
//进行初始化 Configuration.init();
}我们重点关注,获取配置属性。最后进入
com.atomikos.icatch.provider.imp.AssemblerImp.initializeProperties()方法。
@Override
public ConfigProperties initializeProperties() {
//读取classpath下的默认配置transactions-defaults.properties Properties defaults = new Properties();
loadPropertiesFromClasspath(defaults, DEFAULT_PROPERTIES_FILE_NAME);
//读取classpath下,transactions.properties配置,覆盖transactions-defaults.properties中相同key的值 Properties transactionsProperties = new Properties(defaults);
loadPropertiesFromClasspath(transactionsProperties, TRANSACTIONS_PROPERTIES_FILE_NAME);
//读取classpath下,jta.properties,覆盖transactions-defaults.properties、transactions.properties中相同key的值 Properties jtaProperties = new Properties(transactionsProperties);
loadPropertiesFromClasspath(jtaProperties, JTA_PROPERTIES_FILE_NAME);
//读取通过java -Dcom.atomikos.icatch.file方式指定的自定义配置文件路径,覆盖之前的同名配置 Properties customProperties = new Properties(jtaProperties);
loadPropertiesFromCustomFilePath(customProperties);
//最终构造一个ConfigProperties对象,来表示实际要使用的配置 Properties finalProperties = new Properties(customProperties);
return new ConfigProperties(finalProperties);
}接下来重点关注,
Configuration.init(), 进行初始化。
ublic static synchronized boolean init() {
boolean startupInitiated = false;
if (service_ == null) {
startupInitiated = true;
//SPI方式加载插件注册,无需过多关心 addAllTransactionServicePluginServicesFromClasspath();
ConfigProperties configProperties = getConfigProperties();
//调用插件的beforeInit方法进行初始化话,无需过多关心 notifyBeforeInit(configProperties);
//进行事务日志恢复的初始化,很重要,接下来详解 assembleSystemComponents(configProperties);
//进入系统注解的初始化,一般重要 initializeSystemComponents(configProperties);
notifyAfterInit();
if (configProperties.getForceShutdownOnVmExit()) {
addShutdownHook(new ForceShutdownHook());
}
}
return startupInitiated;
}我们先来关注
assembleSystemComponents(configProperties);进入它,进入com.atomikos.icatch.provider.imp.AssemblerImp.assembleTransactionService()方法:
@Override
public TransactionServiceProvider assembleTransactionService(
ConfigProperties configProperties) {
RecoveryLog recoveryLog =null;
//打印日志 logProperties(configProperties.getCompletedProperties());
//生成唯一名字 String tmUniqueName = configProperties.getTmUniqueName();
long maxTimeout = configProperties.getMaxTimeout();
int maxActives = configProperties.getMaxActives();
boolean threaded2pc = configProperties.getThreaded2pc();
//SPI方式加载OltpLog ,这是最重要的扩展地方,如果用户没有SPI的方式去扩展那么就为null OltpLog oltpLog = createOltpLogFromClasspath();
if (oltpLog == null) {
LOGGER.logInfo("Using default (local) logging and recovery...");
//创建事务日志存储资源 Repository repository = createRepository(configProperties);
oltpLog = createOltpLog(repository);
//??? Assemble recoveryLog recoveryLog = createRecoveryLog(repository);
}
StateRecoveryManagerImp recoveryManager = new StateRecoveryManagerImp();
recoveryManager.setOltpLog(oltpLog);
//生成唯一id生成器,以后生成XID会用的到 UniqueIdMgr idMgr = new UniqueIdMgr ( tmUniqueName );
int overflow = idMgr.getMaxIdLengthInBytes() - MAX_TID_LENGTH;
if ( overflow > 0 ) {
// see case 73086 String msg = "Value too long : " + tmUniqueName;
LOGGER.logFatal ( msg );
throw new SysException(msg);
}
return new TransactionServiceImp(tmUniqueName, recoveryManager, idMgr, maxTimeout, maxActives, !threaded2pc, recoveryLog);
}我们重点来分析
createOltpLogFromClasspath(), 采用SPI的加载方式来获取,默认这里会返回null, 什么意思呢? 就是当没有扩展的时候,atomikos,会创建框架自定义的资源,来存储事务日志。
private OltpLog createOltpLogFromClasspath() {
OltpLog ret = null;
ServiceLoader<OltpLogFactory> loader = ServiceLoader.load(OltpLogFactory.class,Configuration.class.getClassLoader());
int i = 0;
for (OltpLogFactory l : loader ) {
ret = l.createOltpLog();
i++;
}
if (i > 1) {
String msg = "More than one OltpLogFactory found in classpath - error in configuration!";
LOGGER.logFatal(msg);
throw new SysException(msg);
}
return ret;
}我们跟着进入
Repository repository = createRepository(configProperties);
private CachedRepository createCoordinatorLogEntryRepository(
ConfigProperties configProperties) throws LogException {
//创建内存资源存储 InMemoryRepository inMemoryCoordinatorLogEntryRepository = new InMemoryRepository();
//进行初始化 inMemoryCoordinatorLogEntryRepository.init();
//创建使用文件存储资源作为backup FileSystemRepository backupCoordinatorLogEntryRepository = new FileSystemRepository();
//进行初始化 backupCoordinatorLogEntryRepository.init();
//内存与file资源进行合并 CachedRepository repository = new CachedRepository(inMemoryCoordinatorLogEntryRepository, backupCoordinatorLogEntryRepository);
repository.init();
return repository;
}这里就会创建出
CachedRepository,里面包含了InMemoryRepository与FileSystemRepository回到主线
com.atomikos.icatch.config.Configuration.init(), 最后来分析下notifyAfterInit();
private static void notifyAfterInit() {
//进行插件的初始化 for (TransactionServicePlugin p : tsListenersList_) {
p.afterInit();
}
for (LogAdministrator a : logAdministrators_) {
a.registerLogControl(service_.getLogControl());
}
//设置事务恢复服务,进行事务的恢复 for (RecoverableResource r : resourceList_ ) {
r.setRecoveryService(recoveryService_);
}
}插件的初始化会进入
com.atomikos.icatch.jta.JtaTransactionServicePlugin.afterInit()
public void afterInit() {
TransactionManagerImp.installTransactionManager(Configuration.getCompositeTransactionManager(), autoRegisterResources);
//如果我们自定义扩展了 OltpLog ,这里就会返回null,如果是null,那么XaResourceRecoveryManager就是null RecoveryLog recoveryLog = Configuration.getRecoveryLog();
long maxTimeout = Configuration.getConfigProperties().getMaxTimeout();
if (recoveryLog != null) {
XaResourceRecoveryManager.installXaResourceRecoveryManager(new DefaultXaRecoveryLog(recoveryLog, maxTimeout),Configuration.getConfigProperties().getTmUniqueName());
}
}重点注意
RecoveryLog recoveryLog = Configuration.getRecoveryLog();,如果用户采用SPI的方式,扩展了com.atomikos.recovery.OltpLog,这里就会返回 null。 如果是null,则不会对XaResourceRecoveryManager进行初始化。回到
notifyAfterInit(), 我们来分析setRecoveryService。
public void setRecoveryService ( RecoveryService recoveryService )
throws ResourceException
{
if ( recoveryService != null ) {
if ( LOGGER.isTraceEnabled() ) LOGGER.logTrace ( "Installing recovery service on resource "
+ getName () );
this.branchIdentifier=recoveryService.getName();
recover();
}
}我们进入
recover()方法:
public void recover() {
XaResourceRecoveryManager xaResourceRecoveryManager = XaResourceRecoveryManager.getInstance();
//null for LogCloud recovery if (xaResourceRecoveryManager != null) {
try {
xaResourceRecoveryManager.recover(getXAResource());
} catch (Exception e) {
refreshXAResource(); //cf case 156968 }
}
}看到最关键的注释了吗,如果用户采用
SPI的方式,扩展了com.atomikos.recovery.OltpLog,那么XaResourceRecoveryManager为null,则就会进行云端恢复,反之则进行事务恢复。 事务恢复很复杂,我们会单独来讲。
到这里atomikos的基本的初始化已经完成。
atomikos事务begin流程
我们知道,本地的事务,都会有一个 trainsaction.begin, 对应XA分布式事务来说也不另外,我们再把思路切换回XAShardingTransactionManager.begin(), 会调用com.atomikos.icatch.jta.TransactionManagerImp.begin()。流程图如下:
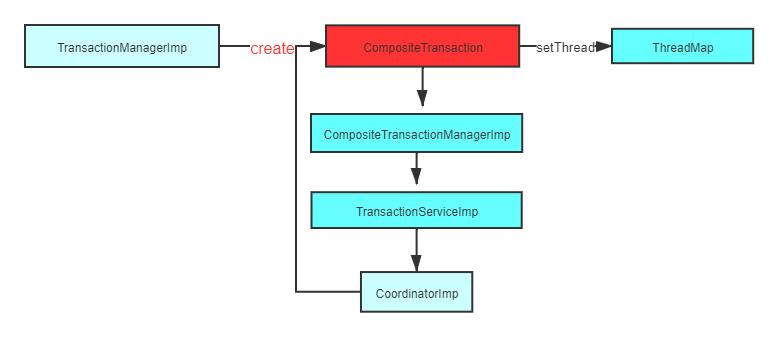
代码:
public void begin ( int timeout ) throws NotSupportedException,
SystemException
{
CompositeTransaction ct = null;
ResumePreviousTransactionSubTxAwareParticipant resumeParticipant = null;
ct = compositeTransactionManager.getCompositeTransaction();
if ( ct != null && ct.getProperty ( JTA_PROPERTY_NAME ) == null ) {
LOGGER.logWarning ( "JTA: temporarily suspending incompatible transaction: " + ct.getTid() +
" (will be resumed after JTA transaction ends)" );
ct = compositeTransactionManager.suspend();
resumeParticipant = new ResumePreviousTransactionSubTxAwareParticipant ( ct );
}
try {
//创建事务补偿点 ct = compositeTransactionManager.createCompositeTransaction ( ( ( long ) timeout ) * 1000 );
if ( resumeParticipant != null ) ct.addSubTxAwareParticipant ( resumeParticipant );
if ( ct.isRoot () && getDefaultSerial () )
ct.setSerial ();
ct.setProperty ( JTA_PROPERTY_NAME , "true" );
} catch ( SysException se ) {
String msg = "Error in begin()";
LOGGER.logError( msg , se );
throw new ExtendedSystemException ( msg , se );
}
recreateCompositeTransactionAsJtaTransaction(ct);
}这里我们主要关注
compositeTransactionManager.createCompositeTransaction(),
public CompositeTransaction createCompositeTransaction ( long timeout ) throws SysException
{
CompositeTransaction ct = null , ret = null;
ct = getCurrentTx ();
if ( ct == null ) {
ret = getTransactionService().createCompositeTransaction ( timeout );
if(LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()){
LOGGER.logDebug("createCompositeTransaction ( " + timeout + " ): "
+ "created new ROOT transaction with id " + ret.getTid ());
}
} else {
if(LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) LOGGER.logDebug("createCompositeTransaction ( " + timeout + " )");
ret = ct.createSubTransaction ();
}
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread ();
setThreadMappings ( ret, thread );
return ret;
}创建了事务补偿点,然后把他放到了用当前线程作为key的Map当中,这里思考,
为啥它不用 threadLocal。
到这里atomikos的事务begin流程已经完成。 大家可能有些疑惑,begin好像什么都没有做,XA start 也没调用? 别慌,下一节继续来讲。
XATransactionDataSource getConnection() 流程
我们都知道想要执行SQL语句,必须要获取到数据库的connection。让我们再回到 XAShardingTransactionManager.getConnection() 最后会调用到org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.xa.jta.datasourceXATransactionDataSource.getConnection()。流程图如下:
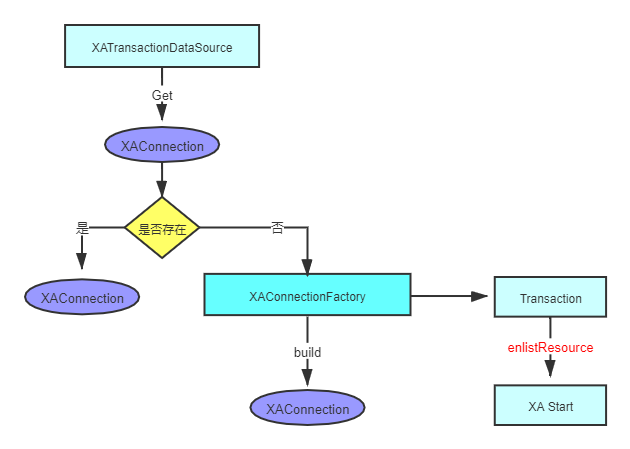
代码 :
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException, SystemException, RollbackException {
//先检查是否已经有存在的connection,这一步很关心,也是XA的关键,因为XA事务,必须在同一个connection if (CONTAINER_DATASOURCE_NAMES.contains(dataSource.getClass().getSimpleName())) {
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
//获取数据库连接 Connection result = dataSource.getConnection();
//转成XAConnection,其实是同一个连接 XAConnection xaConnection = XAConnectionFactory.createXAConnection(databaseType, xaDataSource, result);
//获取JTA事务定义接口 Transaction transaction = xaTransactionManager.getTransactionManager().getTransaction();
if (!enlistedTransactions.get().contains(transaction)) {
//进行资源注册 transaction.enlistResource(new SingleXAResource(resourceName, xaConnection.getXAResource()));
transaction.registerSynchronization(new Synchronization() {
@Override
public void beforeCompletion() {
enlistedTransactions.get().remove(transaction);
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(final int status) {
enlistedTransactions.get().clear();
}
});
enlistedTransactions.get().add(transaction);
}
return result;
}首先第一步很关心,尤其是对shardingsphere来说,因为在一个事务里面,会有多个SQL语句,打到相同的数据库,所以对相同的数据库,必须获取同一个XAConnection,这样才能进行XA事务的提交与回滚。
我们接下来关心
transaction.enlistResource(new SingleXAResource(resourceName, xaConnection.getXAResource()));, 会进入com.atomikos.icatch.jta.TransactionImp.enlistResource(), 代码太长,截取一部分。
try {
restx = (XAResourceTransaction) res
.getResourceTransaction(this.compositeTransaction);
// next, we MUST set the xa resource again, // because ONLY the instance we got as argument // is available for use now ! // older instances (set in restx from previous sibling) // have connections that may be in reuse already // ->old xares not valid except for 2pc operations
restx.setXAResource(xares);
restx.resume();
} catch (ResourceException re) {
throw new ExtendedSystemException(
"Unexpected error during enlist", re);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
}
addXAResourceTransaction(restx, xares);我们直接看
restx.resume();
public synchronized void resume() throws ResourceException {
int flag = 0;
String logFlag = "";
if (this.state.equals(TxState.LOCALLY_DONE)) {// reused instance flag = XAResource.TMJOIN;
logFlag = "XAResource.TMJOIN";
} else if (!this.knownInResource) {// new instance flag = XAResource.TMNOFLAGS;
logFlag = "XAResource.TMNOFLAGS";
} else
throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong state for resume: "
+ this.state);
try {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.logDebug("XAResource.start ( " + this.xidToHexString
+ " , " + logFlag + " ) on resource "
+ this.resourcename
+ " represented by XAResource instance "
+ this.xaresource);
}
this.xaresource.start(this.xid, flag);
} catch (XAException xaerr) {
String msg = interpretErrorCode(this.resourcename, "resume",
this.xid, xaerr.errorCode);
LOGGER.logWarning(msg, xaerr);
throw new ResourceException(msg, xaerr);
}
setState(TxState.ACTIVE);
this.knownInResource = true;
}哦多尅,看见了吗,各位,看见了
this.xaresource.start(this.xid, flag);了吗????,我们进去,假设我们使用的Mysql数据库:
public void start(Xid xid, int flags) throws XAException {
StringBuilder commandBuf = new StringBuilder(300);
commandBuf.append("XA START ");
appendXid(commandBuf, xid);
switch(flags) {
case 0:
break;
case 2097152:
commandBuf.append(" JOIN");
break;
case 134217728:
commandBuf.append(" RESUME");
break;
default:
throw new XAException(-5);
}
this.dispatchCommand(commandBuf.toString());
this.underlyingConnection.setInGlobalTx(true);
}组装
XA start XidSQL语句,进行执行。
到这里,我们总结下,在获取数据库连接的时候,我们执行了XA协议接口中的 XA start xid
atomikos事务commit流程
好了,上面我们已经开启了事务,现在我们来分析下事务commit流程,我们再把视角切换回XAShardingTransactionManager.commit(),最后我们会进入com.atomikos.icatch.imp.CompositeTransactionImp.commit() 方法。流程图如下:
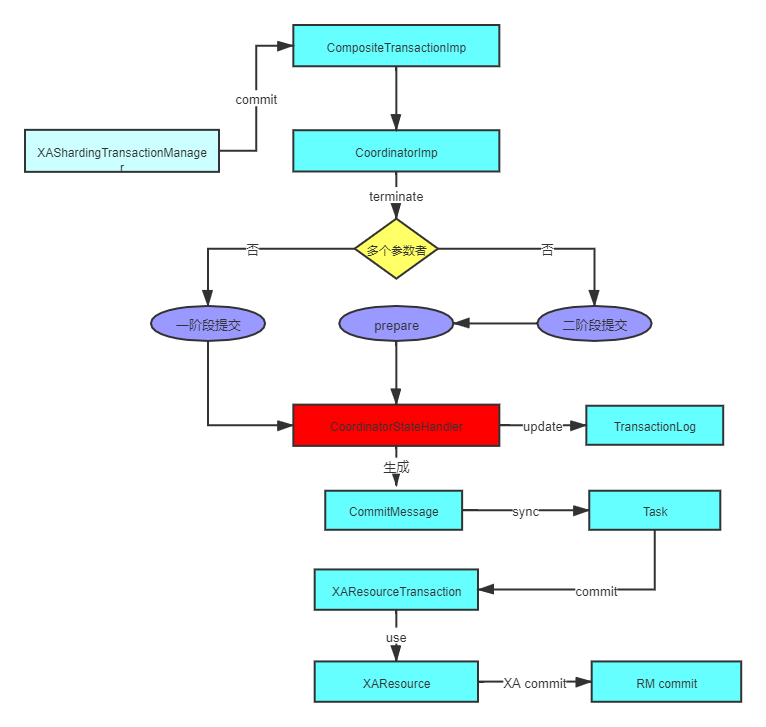
代码:
public void commit () throws HeurRollbackException, HeurMixedException,
HeurHazardException, SysException, SecurityException,
RollbackException
{
//首先更新下事务日志的状态 doCommit ();
setSiblingInfoForIncoming1pcRequestFromRemoteClient();
if ( isRoot () ) {
//真正的commit操作 coordinator.terminate ( true );
}
}我们关注
coordinator.terminate ( true );
protected void terminate ( boolean commit ) throws HeurRollbackException,
HeurMixedException, SysException, java.lang.SecurityException,
HeurCommitException, HeurHazardException, RollbackException,
IllegalStateException
{
synchronized ( fsm_ ) {
if ( commit ) {
//判断有几个参与者,如果只有一个,直接提交 if ( participants_.size () <= 1 ) {
commit ( true );
} else {
//否则,走XA 2阶段提交流程,先prepare, 再提交 int prepareResult = prepare ();
// make sure to only do commit if NOT read only if ( prepareResult != Participant.READ_ONLY )
commit ( false );
}
} else {
rollback ();
}
}
}首先会判断参与者的个数,这里我们可以理解为MySQL的database数量,如果只有一个,退化成一阶段,直接提交。 如果有多个,则走标准的XA二阶段提交流程。
我们来看
prepare ();流程,最后会走到com.atomikos.icatch.imp.PrepareMessage.send()--->com.atomikos.datasource.xa.XAResourceTransaction.prepare()
int ret = 0;
terminateInResource();
if (TxState.ACTIVE == this.state) {
// tolerate non-delisting apps/servers suspend();
}
// duplicate prepares can happen for siblings in serial subtxs!!! // in that case, the second prepare just returns READONLY if (this.state == TxState.IN_DOUBT)
return Participant.READ_ONLY;
else if (!(this.state == TxState.LOCALLY_DONE))
throw new SysException("Wrong state for prepare: " + this.state);
try {
// refresh xaresource for MQSeries: seems to close XAResource after // suspend??? testOrRefreshXAResourceFor2PC();
if (LOGGER.isTraceEnabled()) {
LOGGER.logTrace("About to call prepare on XAResource instance: "
+ this.xaresource);
}
ret = this.xaresource.prepare(this.xid);
} catch (XAException xaerr) {
String msg = interpretErrorCode(this.resourcename, "prepare",
this.xid, xaerr.errorCode);
if (XAException.XA_RBBASE <= xaerr.errorCode
&& xaerr.errorCode <= XAException.XA_RBEND) {
LOGGER.logWarning(msg, xaerr); // see case 84253 throw new RollbackException(msg);
} else {
LOGGER.logError(msg, xaerr);
throw new SysException(msg, xaerr);
}
}
setState(TxState.IN_DOUBT);
if (ret == XAResource.XA_RDONLY) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.logDebug("XAResource.prepare ( " + this.xidToHexString
+ " ) returning XAResource.XA_RDONLY " + "on resource "
+ this.resourcename
+ " represented by XAResource instance "
+ this.xaresource);
}
return Participant.READ_ONLY;
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.logDebug("XAResource.prepare ( " + this.xidToHexString
+ " ) returning OK " + "on resource "
+ this.resourcename
+ " represented by XAResource instance "
+ this.xaresource);
}
return Participant.READ_ONLY + 1;
}终于,我们看到了这么一句
ret = this.xaresource.prepare(this.xid);但是等等,我们之前不是说了,XA start xid以后要先XA end xid吗? 答案就在suspend();里面。
public synchronized void suspend() throws ResourceException {
// BugzID: 20545 // State may be IN_DOUBT or TERMINATED when a connection is closed AFTER // commit! // In that case, don't call END again, and also don't generate any // error! // This is required for some hibernate connection release strategies. if (this.state.equals(TxState.ACTIVE)) {
try {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.logDebug("XAResource.end ( " + this.xidToHexString
+ " , XAResource.TMSUCCESS ) on resource "
+ this.resourcename
+ " represented by XAResource instance "
+ this.xaresource);
}
//执行了 xa end 语句 this.xaresource.end(this.xid, XAResource.TMSUCCESS);
} catch (XAException xaerr) {
String msg = interpretErrorCode(this.resourcename, "end",
this.xid, xaerr.errorCode);
if (LOGGER.isTraceEnabled())
LOGGER.logTrace(msg, xaerr);
// don't throw: fix for case 102827 }
setState(TxState.LOCALLY_DONE);
}
}到了这里,我们已经执行了 XA start xid -> XA end xid --> XA prepare xid, 接下来就是最后一步 commit
我们再回到
terminate(false)方法,来看 commit()流程。其实和 prepare流程一样,最后会走到com.atomikos.datasource.xa.XAResourceTransaction.commit()。 commit执行完,数据提交
//繁杂代码过多,就显示核心的this.xaresource.commit(this.xid, onePhase);
思考:这里的参与者提交是在一个循环里面,一个一个提交的,如果之前的提交了,后面的参与者提交的时候,挂了,就会造成数据的不一致性。
Atomikos rollback() 流程
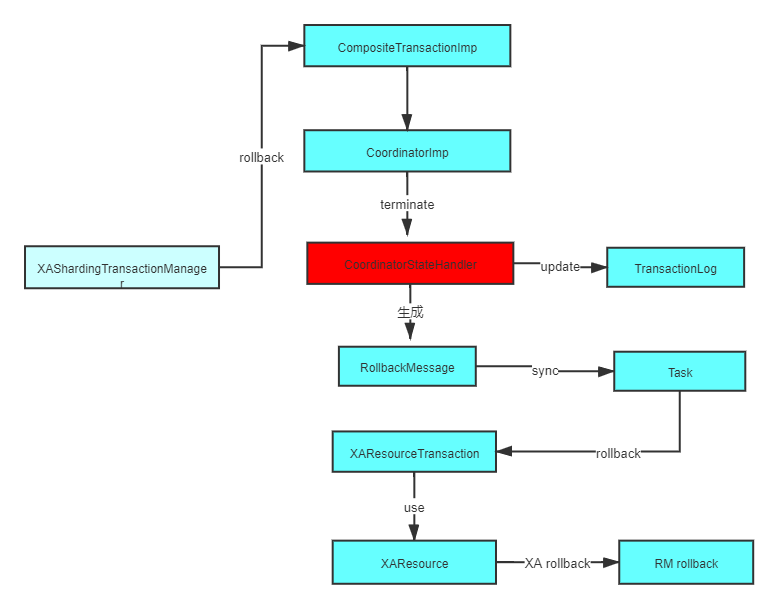
上面我们已经分析了commit流程,其实rollback流程和commit流程一样,我们在把目光切换回 org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.xa.XAShardingTransactionManager.rollback() ,最后会执行到com.atomikos.icatch.imp.CompositeTransactionImp.rollback()。
public void rollback () throws IllegalStateException, SysException
{
//清空资源,更新事务日志状态等 doRollback ();
if ( isRoot () ) {
try {
coordinator.terminate ( false );
} catch ( Exception e ) {
throw new SysException ( "Unexpected error in rollback: " + e.getMessage (), e );
}
}
}重点关注
coordinator.terminate ( false );,这个和 commit流程是一样的,只不过在 commit流程里面,参数传的是true。
protected void terminate ( boolean commit ) throws HeurRollbackException,
HeurMixedException, SysException, java.lang.SecurityException,
HeurCommitException, HeurHazardException, RollbackException,
IllegalStateException
{
synchronized ( fsm_ ) {
if ( commit ) {
if ( participants_.size () <= 1 ) {
commit ( true );
} else {
int prepareResult = prepare ();
// make sure to only do commit if NOT read only if ( prepareResult != Participant.READ_ONLY )
commit ( false );
}
} else {
//如果是false,走的是rollback rollback ();
}
}
}我们重点关注
rollback(),最后会走到com.atomikos.datasource.xa.XAResourceTransaction.rollback()。
public synchronized void rollback()
throws HeurCommitException, HeurMixedException,
HeurHazardException, SysException {
terminateInResource();
if (rollbackShouldDoNothing()) {
return;
}
if (this.state.equals(TxState.TERMINATED)) {
return;
}
if (this.state.equals(TxState.HEUR_MIXED))
throw new HeurMixedException();
if (this.state.equals(TxState.HEUR_COMMITTED))
throw new HeurCommitException();
if (this.xaresource == null) {
throw new HeurHazardException("XAResourceTransaction "
+ getXid() + ": no XAResource to rollback?");
}
try {
if (this.state.equals(TxState.ACTIVE)) { // first suspend xid suspend();
}
// refresh xaresource for MQSeries: seems to close XAResource after // suspend??? testOrRefreshXAResourceFor2PC();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.logDebug("XAResource.rollback ( " + this.xidToHexString
+ " ) " + "on resource " + this.resourcename
+ " represented by XAResource instance "
+ this.xaresource);
}
this.xaresource.rollback(this.xid);先在supend()方法里面执行了 XA end xid 语句, 接下来执行 this.xaresource.rollback(this.xid); 进行数据的回滚。
Atomikos-recover 流程
说事务恢复流程之前,我们来讨论下,会啥会出现事务恢复?XA二阶段提交协议不是强一致性的吗?要解答这个问题,我们就要来看看XA二阶段协议有什么问题?
问题一 :单点故障
由于协调者的重要性,一旦协调者TM发生故障。参与者RM会一直阻塞下去。尤其在第二阶段,协调者发生故障,那么所有的参与者还都处于锁定事务资源的状态中,而无法继续完成事务操作。(如果是协调者挂掉,可以重新选举一个协调者,但是无法解决因为协调者宕机导致的参与者处于阻塞状态的问题)
问题二 :数据不一致
数据不一致。在二阶段提交的阶段二中,当协调者向参与者发送commit请求之后,发生了局部网络异常或者在发送commit请求过程中协调者发生了故障,这回导致只有一部分参与者接受到了commit请求。而在这部分参与者接到commit请求之后就会执行commit操作。但是其他部分未接到commit请求的机器则无法执行事务提交。于是整个分布式系统便出现了数据不一致性的现象。
如何解决?
解决的方案简单,就是我们在事务的操作的每一步,我们都需要对事务状态的日志进行人为的记录,我们可以把日志记录存储在我们想存储的地方,可以是本地存储,也可以中心化的存储。atomikos的开源版本,我们之前也分析了,它是使用内存 + file的方式,存储在本地,这样的话,如果在一个集群系统里面,如果有节点宕机,日志又存储在本地,所以事务不能及时的恢复(需要重启服务)。
Atomikos 多场景下事务恢复。
Atomikos 提供了二种方式,来应对不同场景下的异常情况。
场景一: 服务节点不宕机,因为其他的原因,产生需要事务恢复的情况。 这个时候才要定时任务进行恢复。 具体的代码
com.atomikos.icatch.imp.TransactionServiceImp.init()方法,会初始化一个定时任务,进行事务的恢复。
public synchronized void init ( Properties properties ) throws SysException
{
shutdownInProgress_ = false;
control_ = new com.atomikos.icatch.admin.imp.LogControlImp ( (AdminLog) this.recoveryLog );
ConfigProperties configProperties = new ConfigProperties(properties);
long recoveryDelay = configProperties.getRecoveryDelay();
recoveryTimer = new PooledAlarmTimer(recoveryDelay);
recoveryTimer.addAlarmTimerListener(new AlarmTimerListener() {
@Override
public void alarm(AlarmTimer timer) {
//进行事务恢复 performRecovery();
}
});
TaskManager.SINGLETON.executeTask(recoveryTimer);
initialized_ = true;
}最终会进入
com.atomikos.datasource.xa.XATransactionalResource.recover()方法。
public void recover() {
XaResourceRecoveryManager xaResourceRecoveryManager = XaResourceRecoveryManager.getInstance();
if (xaResourceRecoveryManager != null) { //null for LogCloud recovery try {
xaResourceRecoveryManager.recover(getXAResource());
} catch (Exception e) {
refreshXAResource(); //cf case 156968 }
}
}场景二: 当服务节点宕机重启动过程中进行事务的恢复。具体实现在
com.atomikos.datasource.xa.XATransactionalResource.setRecoveryService()方法里面
@Override
public void setRecoveryService ( RecoveryService recoveryService )
throws ResourceException
{
if ( recoveryService != null ) {
if ( LOGGER.isTraceEnabled() ) LOGGER.logTrace ( "Installing recovery service on resource "
+ getName () );
this.branchIdentifier=recoveryService.getName();
//进行事务恢复 recover();
}
}com.atomikos.datasource.xa.XATransactionalResource.recover() 流程详解。
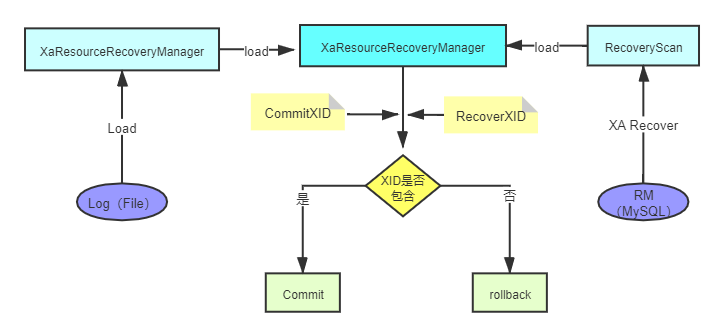
主代码:
public void recover(XAResource xaResource) throws XAException {
// 根据XA recovery 协议获取 xid List<XID> xidsToRecover = retrievePreparedXidsFromXaResource(xaResource);
Collection<XID> xidsToCommit;
try {
// xid 与日志记录的xid进行匹配 xidsToCommit = retrieveExpiredCommittingXidsFromLog();
for (XID xid : xidsToRecover) {
if (xidsToCommit.contains(xid)) {
//执行 XA commit xid 进行提交 replayCommit(xid, xaResource);
} else {
attemptPresumedAbort(xid, xaResource);
}
}
} catch (LogException couldNotRetrieveCommittingXids) {
LOGGER.logWarning("Transient error while recovering - will retry later...", couldNotRetrieveCommittingXids);
}
}我们来看一下如何根据
XA recovery 协议获取RM端存储的xid。 进入方法retrievePreparedXidsFromXaResource(xaResource), 最后进入com.atomikos.datasource.xa.RecoveryScan.recoverXids()方法。
public static List<XID> recoverXids(XAResource xaResource, XidSelector selector) throws XAException {
List<XID> ret = new ArrayList<XID>();
boolean done = false;
int flags = XAResource.TMSTARTRSCAN;
Xid[] xidsFromLastScan = null;
List<XID> allRecoveredXidsSoFar = new ArrayList<XID>();
do {
xidsFromLastScan = xaResource.recover(flags);
flags = XAResource.TMNOFLAGS;
done = (xidsFromLastScan == null || xidsFromLastScan.length == 0);
if (!done) {
// TEMPTATIVELY SET done TO TRUE // TO TOLERATE ORACLE 8.1.7 INFINITE // LOOP (ALWAYS RETURNS SAME RECOVER // SET). IF A NEW SET OF XIDS IS RETURNED // THEN done WILL BE RESET TO FALSE done = true;
for ( int i = 0; i < xidsFromLastScan.length; i++ ) {
XID xid = new XID ( xidsFromLastScan[i] );
// our own XID implements equals and hashCode properly if (!allRecoveredXidsSoFar.contains(xid)) {
// a new xid is returned -> we can not be in a recovery loop -> go on allRecoveredXidsSoFar.add(xid);
done = false;
if (selector.selects(xid)) {
ret.add(xid);
}
}
}
}
} while (!done);
return ret;
}我们重点关注
xidsFromLastScan = xaResource.recover(flags);这个方法,如果我们使用MySQL,那么久会进入 MysqlXAConnection.recover()方法。执行XA recovery xid语句来获取 xid。
protected static Xid[] recover(Connection c, int flag) throws XAException {
/* * The XA RECOVER statement returns information for those XA transactions on the MySQL server that are in the PREPARED state. (See Section 13.4.7.2, ???XA * Transaction States???.) The output includes a row for each such XA transaction on the server, regardless of which client started it. * * XA RECOVER output rows look like this (for an example xid value consisting of the parts 'abc', 'def', and 7): * * mysql> XA RECOVER; * +----------+--------------+--------------+--------+ * | formatID | gtrid_length | bqual_length | data | * +----------+--------------+--------------+--------+ * | 7 | 3 | 3 | abcdef | * +----------+--------------+--------------+--------+ * * The output columns have the following meanings: * * formatID is the formatID part of the transaction xid * gtrid_length is the length in bytes of the gtrid part of the xid * bqual_length is the length in bytes of the bqual part of the xid * data is the concatenation of the gtrid and bqual parts of the xid */
boolean startRscan = ((flag & TMSTARTRSCAN) > 0);
boolean endRscan = ((flag & TMENDRSCAN) > 0);
if (!startRscan && !endRscan && flag != TMNOFLAGS) {
throw new MysqlXAException(XAException.XAER_INVAL, Messages.getString("MysqlXAConnection.001"), null);
}
// // We return all recovered XIDs at once, so if not TMSTARTRSCAN, return no new XIDs // // We don't attempt to maintain state to check for TMNOFLAGS "outside" of a scan //
if (!startRscan) {
return new Xid[0];
}
ResultSet rs = null;
Statement stmt = null;
List<MysqlXid> recoveredXidList = new ArrayList<MysqlXid>();
try {
// TODO: Cache this for lifetime of XAConnection stmt = c.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery("XA RECOVER");
while (rs.next()) {
final int formatId = rs.getInt(1);
int gtridLength = rs.getInt(2);
int bqualLength = rs.getInt(3);
byte[] gtridAndBqual = rs.getBytes(4);
final byte[] gtrid = new byte[gtridLength];
final byte[] bqual = new byte[bqualLength];
if (gtridAndBqual.length != (gtridLength + bqualLength)) {
throw new MysqlXAException(XAException.XA_RBPROTO, Messages.getString("MysqlXAConnection.002"), null);
}
System.arraycopy(gtridAndBqual, 0, gtrid, 0, gtridLength);
System.arraycopy(gtridAndBqual, gtridLength, bqual, 0, bqualLength);
recoveredXidList.add(new MysqlXid(gtrid, bqual, formatId));
}
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
throw mapXAExceptionFromSQLException(sqlEx);
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
throw mapXAExceptionFromSQLException(sqlEx);
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
throw mapXAExceptionFromSQLException(sqlEx);
}
}
}
int numXids = recoveredXidList.size();
Xid[] asXids = new Xid[numXids];
Object[] asObjects = recoveredXidList.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < numXids; i++) {
asXids[i] = (Xid) asObjects[i];
}
return asXids;
}这里要注意如果Mysql的版本 <5.7.7 ,则不会有任何数据,在以后的版本中Mysql进行了修复,因此如果我们想要使用MySQL充当RM,版本必须 >= 5.7.7,原因是:
MySQL 5.6版本在客户端退出的时候,自动把已经prepare的事务回滚了,那么MySQL为什么要这样做?这主要取决于MySQL的内部实现,MySQL 5.7以前的版本,对于prepare的事务,MySQL是不会记录binlog的(官方说是减少fsync,起到了优化的作用)。只有当分布式事务提交的时候才会把前面的操作写入binlog信息,所以对于binlog来说,分布式事务与普通的事务没有区别,而prepare以前的操作信息都保存在连接的IO_CACHE中,如果这个时候客户端退出了,以前的binlog信息都会被丢失,再次重连后允许提交的话,会造成Binlog丢失,从而造成主从数据的不一致,所以官方在客户端退出的时候直接把已经prepare的事务都回滚了!
回到主线再从自己记录的事务日志里面获取XID
Collection<XID> xidsToCommit = retrieveExpiredCommittingXidsFromLog();
我们来看下获取事务日志里面的XID的
retrieveExpiredCommittingXidsFromLog()方法。 然后进入com.atomikos.recovery.imp.RecoveryLogImp.getCommittingParticipants()方法。
public Collection<ParticipantLogEntry> getCommittingParticipants()
throws LogReadException {
Collection<ParticipantLogEntry> committingParticipants = new HashSet<ParticipantLogEntry>();
Collection<CoordinatorLogEntry> committingCoordinatorLogEntries = repository.findAllCommittingCoordinatorLogEntries();
for (CoordinatorLogEntry coordinatorLogEntry : committingCoordinatorLogEntries) {
for (ParticipantLogEntry participantLogEntry : coordinatorLogEntry.participants) {
committingParticipants.add(participantLogEntry);
}
}
return committingParticipants;
}到这里我们来简单介绍一下,事务日志的存储结构。首先是 CoordinatorLogEntry,这是一次XA事务的所有信息实体类。
public class CoordinatorLogEntry implements Serializable {
//全局事务id public final String id;
//是否已经提交 public final boolean wasCommitted;
/** * Only for subtransactions, null otherwise. */
public final String superiorCoordinatorId;
//参与者集合 public final ParticipantLogEntry[] participants;}再来看一下参与者实体类
ParticipantLogEntry:
public class ParticipantLogEntry implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1728296701394899871L;
/** * The ID of the global transaction as known by the transaction core. */
public final String coordinatorId;
/** * Identifies the participant within the global transaction. */
public final String uri;
/** * When does this participant expire (expressed in millis since Jan 1, 1970)? */
public final long expires;
/** * Best-known state of the participant. */
public final TxState state;
/** * For diagnostic purposes, null if not relevant. */
public final String resourceName;}回到
com.atomikos.recovery.xa.DefaultXaRecoveryLog.getExpiredCommittingXids()方法,可以到获取了一次XA事务过程中,存储的事务日志中的xid。
public Set<XID> getExpiredCommittingXids() throws LogReadException {
Set<XID> ret = new HashSet<XID>();
Collection<ParticipantLogEntry> entries = log.getCommittingParticipants();
for (ParticipantLogEntry entry : entries) {
if (expired(entry) && !http(entry)) {
XID xid = new XID(entry.coordinatorId, entry.uri);
ret.add(xid);
}
}
return ret;
}如果从RM中通过XA recovery取出的XID,包含在从事务日志中取出的XID,则进行commit,否则进行rollback.
List<XID> xidsToRecover = retrievePreparedXidsFromXaResource(xaResource);
Collection<XID> xidsToCommit;
try {
xidsToCommit = retrieveExpiredCommittingXidsFromLog();
for (XID xid : xidsToRecover) {
if (xidsToCommit.contains(xid)) {
replayCommit(xid, xaResource);
} else {
attemptPresumedAbort(xid, xaResource);
}
}
} catch (LogException couldNotRetrieveCommittingXids) {
LOGGER.logWarning("Transient error while recovering - will retry later...", couldNotRetrieveCommittingXids);
}replayCommit 方法如下:
private void replayCommit(XID xid, XAResource xaResource) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) LOGGER.logDebug("Replaying commit of xid: " + xid);
try {
//进行事务提交 xaResource.commit(xid, false);
//更新事务日志 log.terminated(xid);
} catch (XAException e) {
if (alreadyHeuristicallyTerminatedByResource(e)) {
handleHeuristicTerminationByResource(xid, xaResource, e, true);
} else if (xidTerminatedInResourceByConcurrentCommit(e)) {
log.terminated(xid);
} else {
LOGGER.logWarning("Transient error while replaying commit - will retry later...", e);
}
}
}attemptPresumedAbort(xid, xaResource); 方法如下:
private void attemptPresumedAbort(XID xid, XAResource xaResource) {
try {
log.presumedAborting(xid);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) LOGGER.logDebug("Presumed abort of xid: " + xid);
try {
//进行回滚 xaResource.rollback(xid);
//更新日志状态 log.terminated(xid);
} catch (XAException e) {
if (alreadyHeuristicallyTerminatedByResource(e)) {
handleHeuristicTerminationByResource(xid, xaResource, e, false);
} else if (xidTerminatedInResourceByConcurrentRollback(e)) {
log.terminated(xid);
} else {
LOGGER.logWarning("Unexpected exception during recovery - ignoring to retry later...", e);
}
}
} catch (IllegalStateException presumedAbortNotAllowedInCurrentLogState) {
// ignore to retry later if necessary } catch (LogException logWriteException) {
LOGGER.logWarning("log write failed for Xid: "+xid+", ignoring to retry later", logWriteException);
}
}总结
文章到此,已经写的很长很多了,我们分析了ShardingSphere对于XA方案,提供了一套SPI解决方案,对Atomikos进行了整合,也分析了Atomikos初始化流程,开始事务流程,获取连接流程,提交事务流程,回滚事务流程,事务恢复流程。希望对大家理解XA的原理有所帮助。
加入我们
Apache ShardingSphere 一直践行Apache Way的开源之道,社区完全开放与平等,人人享受开源带来的快乐。
地址: https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere
作者介绍: 肖宇,Apache ShardingSphere Committer,开源hmily分布式事务框架作者, 开源soul网关作者,热爱开源,追求写优雅代码。目前就职入京东数科,参与ShardingSphere的开源建设,以及分布式数据库的研发工作。











