一、前言
在做MySQL的SQL优化时,如果只涉及到单表查询,那么大部分慢SQL都只需从索引上入手优化即可,通过添加合适的索引来消除全表扫描或者排序操作,执行效果,大概率能实现质的飞跃。
然而,在实际生产中,除了单表查询,更多的是多个表的联合查询,这样的查询通常是慢SQL的重灾区,查询速度慢,且使用服务器资源较多,如果能将这类SQL优化掉,那必将大大减轻数据库服务器压力。现在,咱就通过多表关联内部数据操作的角度,看看如何进行SQL优化。
二、准备工作
现在线上环境大部分使用的都是MySQL 5.7.x版本,那咱就以5.7版本为主,适当延伸MySQL 8.0版本为辅进行讲解测试。
创建测试表:
# 创建两个表结构一模一样的表:t1、t2
create table t1(
id int not null auto_increment,
a int,
b int,
c int,
primary key(id),
key idx_a(a)
);
create table t2 like t1;
构造测试数据:
# 创建2个存储过程用于构造测试数据
# 构造t1表数据的存储过程,数据为3的整除数,1000条
delimiter //
create procedure t1_proc()
begin
declare i int default 1;
while (i<=3000) do
if (i%3) = 0 then
insert into t1(a,b,c) values(i, i, i);
end if;
set i=i+1;
end while;
end //
delimiter ;
# 构造t2表数据的存储过程,数据为2的整除数,100000条
delimiter //
create procedure t2_proc()
begin
declare i int default 1;
while (i<=200000) do
if (i%2) = 0 then
insert into t2(a,b,c) values(i, i, i);
end if;
set i=i+1;
end while;
end //
delimiter ;
# 调用存储过程,生成测试数据
call t1_proc();
call t2_proc();
# 删除存储过程
drop procedure t1_proc;
drop procedure t2_proc;
数据样例:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>select * from t1 limit 5;
+----+------+------+------+
| id | a | b | c |
+----+------+------+------+
| 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 3 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| 4 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 5 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
+----+------+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>select * from t2 limit 5;
+----+------+------+------+
| id | a | b | c |
+----+------+------+------+
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 3 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 5 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
+----+------+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
三、MySQL JOIN算法
MySQL对两表关联,支持多种Join算法,咱就以下面这个SQL为例,深入探讨一下。
测试SQL:
select * from t1 join t2 on t1.b=t2.b;
1、Simple Nested-Loop Join
设想一下,如果两表关联,在没有任何干预的情况下,他像不像下面这个伪代码的嵌套循环:
for row_1 in t1: # 循环1000次
for row_2 in t2: # 对应每个外层循环10w次
if row_1.b == row_2.b:
do something
从上面的伪代码中,我们可以看到,其就是简单粗暴的嵌套循环,我们将其称为 Simple Nested-Loop Join。回到数据库层面,在测试SQL两个表关联的过程中,t1表中的每一行数据,都会触发扫描一次t2表的数据,然后进行数据匹配。总的来讲就是,因为t1表有1000行数据,所以t2表会被扫描1000次,并进行1000 * 10w = 1亿次数据比较。
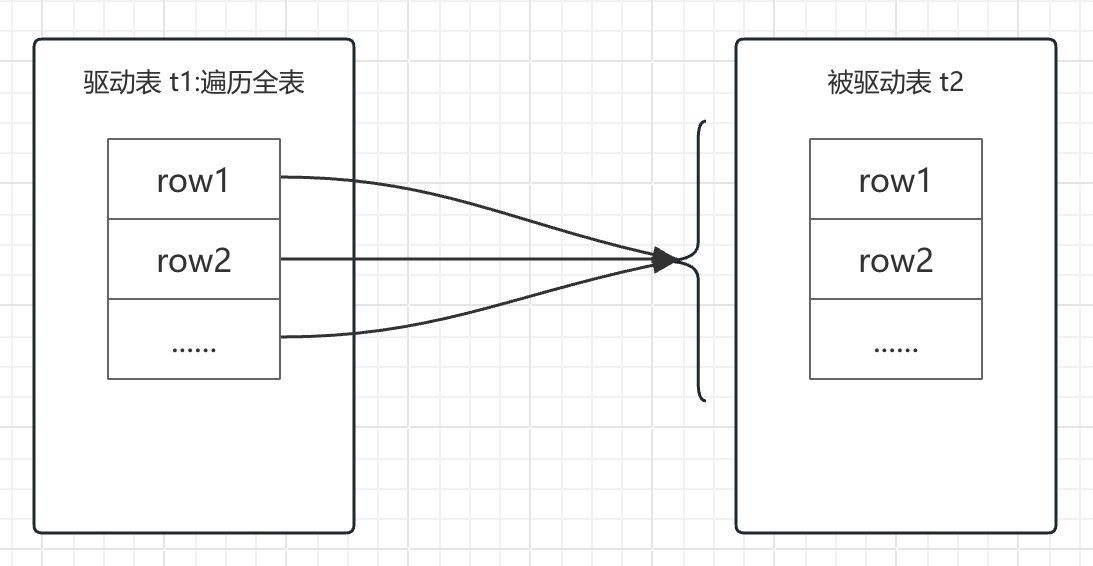
很显然,如果使用这种方式,当 t2 表足够大时,反复扫描数据的过程中,磁盘必然会被拉爆,服务器性能会急剧下降。像MySQL这样优秀的产品,必然会想方设法的避免这种情况的发生。
2、Block Nested-Loop Join
紧接上面所说,既然 Simple Nested-Loop Join最大的弊端是被驱动表被反复扫描,那是不是可以从这方面入手,减少被驱动表的扫描次数,以达到优化目的。咱继续往下看,看他是怎么实现的。
一般情况下,两表关联,MySQL都会将结果集小(指根据条件过滤后)的表做驱动表,结果集大的表当被驱动表,那是不是可以尝试一下,把驱动表的结果集放到内存中(Join Buffer),然后一次性扫描被驱动表的所有数据,反过来与Join Buffer中的驱动表结果集进行比较。这方式,驱动表和被驱动表都只扫描一次,但在内存中进行数据比较的次数依然为 10w * 1000 = 1亿次。很显然,这方式,相对于Simple Nested-Loop Join而言,优势非常明显,MySQL管这个叫Block Nested-Loop Join。
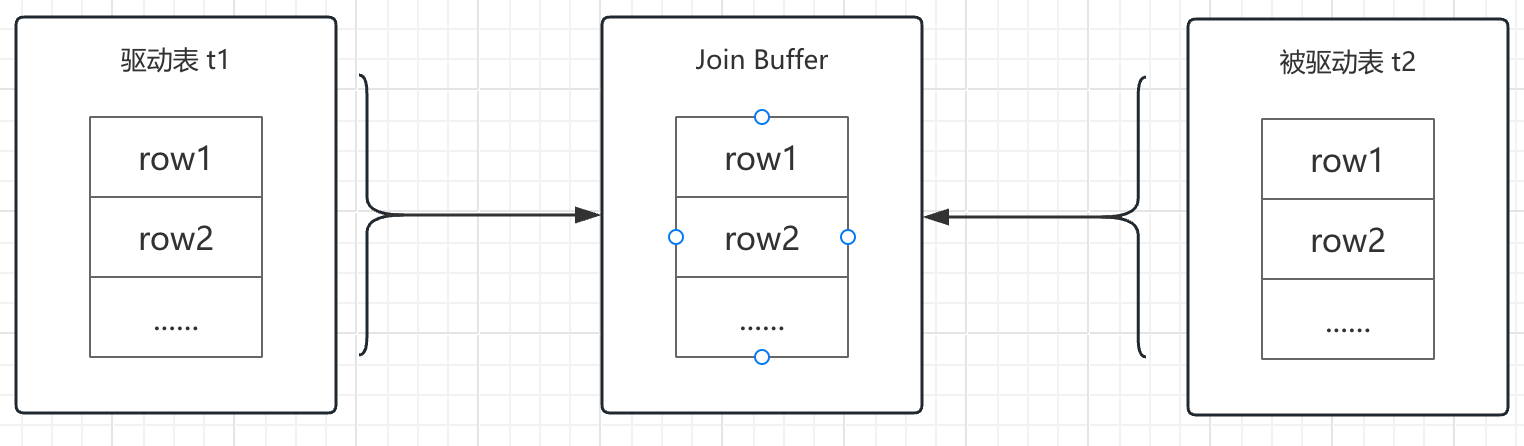
聪明的你,是不是在想:如果驱动表t1的结果集,无法一次性全部存放到Join Buffer内存中时,怎么办?
Join Buffer 的大小由参数 join_buffer_size 控制,默认为256K。在使用Join Buffer时,如果无法一次性存放所有结果集,他会分多次进行,比如:
1)读取驱动表t1的数据,存放到Join Buffer中,假设,存放400条后,Join Buffer满了,停止读取
2)读取被驱动表t2的数据,每一行数据都与Join Buffer中的数据进行比较,并返回符合条件的结果集
3)清空Join Buffer
4)继续读取驱动表t1的数据,将401-800的数据存放到Join Buffer,直到存满
5)...... 继续重复相似的动作,直到所有数据都比对完
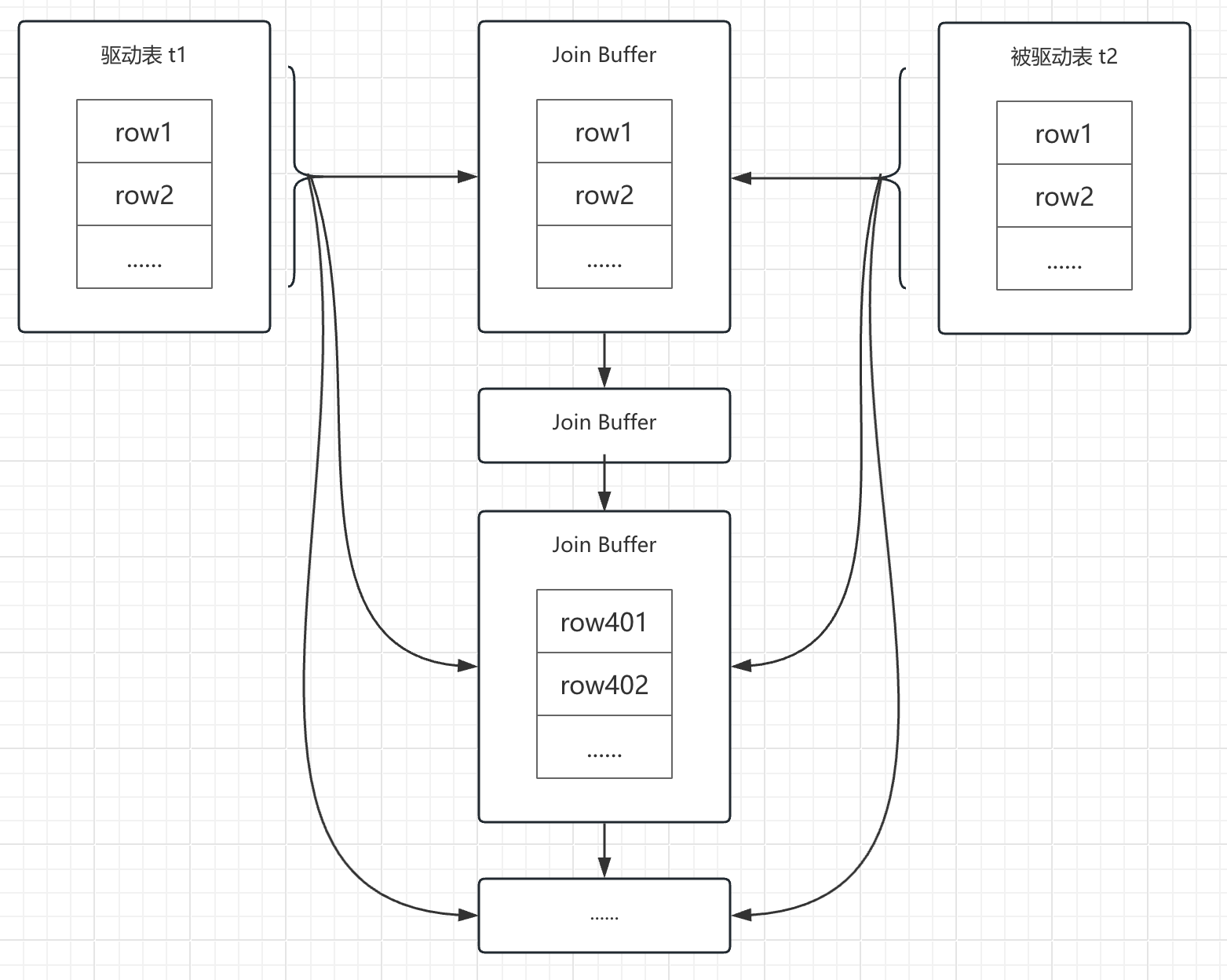
在上述假设情况下,因Join Buffer大小限制的原因,被驱动表 t2 被扫描了3次。总的来讲,虽然不算完美,但显然比使用Simple Nested-Loop Join的方式容易接受多了。也就是说,MySQL在经过对表链接进行优化后,就不会再出现使用Simple Nested-Loop Join的情况了。
执行计划:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>explain select * from t1 join t2 on t1.b=t2.b\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t1
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 1000
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t2
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 100256
filtered: 10.00
Extra: Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop)
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
3、Hash Join
虽然经过MySQL优化后的 Block Nested-Loop Join 算是改进了不少,但是,对各位程序员大拿而言,必然是一眼就看出了还有改进的余地。
Block Nested-Loop Join 在将驱动表结果集存放到Join Buffer后,被驱动表的数据与其比对时,被驱动表的每一行数据,都要与Join Buffer中所有数据进行比对,才能得出匹配的结果。这像不像对MySQL实体表进行条件查询时,进行了全表扫描的操作一样。这情况,如果给条件列加个索引,查询速度是不是要瞬间起飞。
想法很好,但很不幸,MySQL 5.7.x 版本不支持;但也很庆幸,MySQL 8.0版本实现了,他会根据驱动表结果集,将关联列映射为哈希值后键创建哈希表,被驱动表的数据在与哈希表进行比较时,就大大降低了比较次数,这也达到了优化的目的,我们管其叫Hash Join。
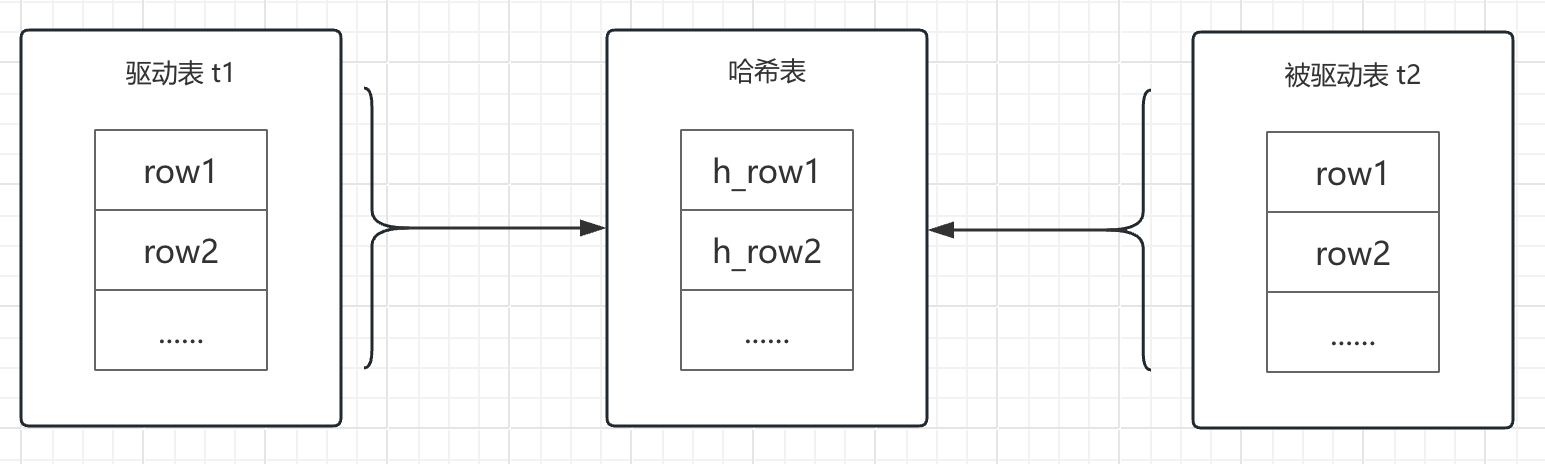
咱看看其执行计划:
[8.0.27 127.0.0.1:3380]>explain select * from t1 join t2 on t1.b=t2.b\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t1
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 1000
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t2
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 100400
filtered: 10.00
Extra: Using where; Using join buffer (hash join)
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
咱再来对比一下Block Nested-Loop Join和Hash Join的执行速度:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>select * from t1 join t2 on t1.b=t2.b;
......
+------+------+------+------+------+------+
500 rows in set (4.90 sec)
[8.0.27 127.0.0.1:3380]>select * from t1 join t2 on t1.b=t2.b;
......
+------+------+------+------+------+------+
500 rows in set (0.02 sec)
从执行逻辑和执行结果上,都印证了Hash Join必然会比Block Nested-Loop Join要好。所以,在MySQL 8.0版本,Block Nested-Loop Join将不复存在,所有原先使用其算法的表关联SQL,最终都会被优化成选择Hash Join进行表关联。
4、Index Nested-Loop Join
前面提到的 Block Nested-Loop Join 和 Hash Join,都是MySQL自己内部实现的优化,如果没有其他更好的算法,那么基于这两种算法基础上的表关联慢SQL,人为干预改进的可能性,是不是就微无其微了。
我们仔细分析一下前面这两种算法的特点,Block Nested-Loop Join 的改进是降低了表扫描次数, Hash Join的改进是降低了数据对比的次数,但他两,依然有一个致命的共同点,如果被驱动表足够大(大表)时,比如有N亿数据量,那么,哪怕扫描一次被驱动表,也会引起数据库性能急剧下降。
知道了问题在哪,自然就有了优化的方向。设想一下,如果被驱动表的关联列,像Hash Join中的哈希表一样,存在索引,会是个什么情况呢?
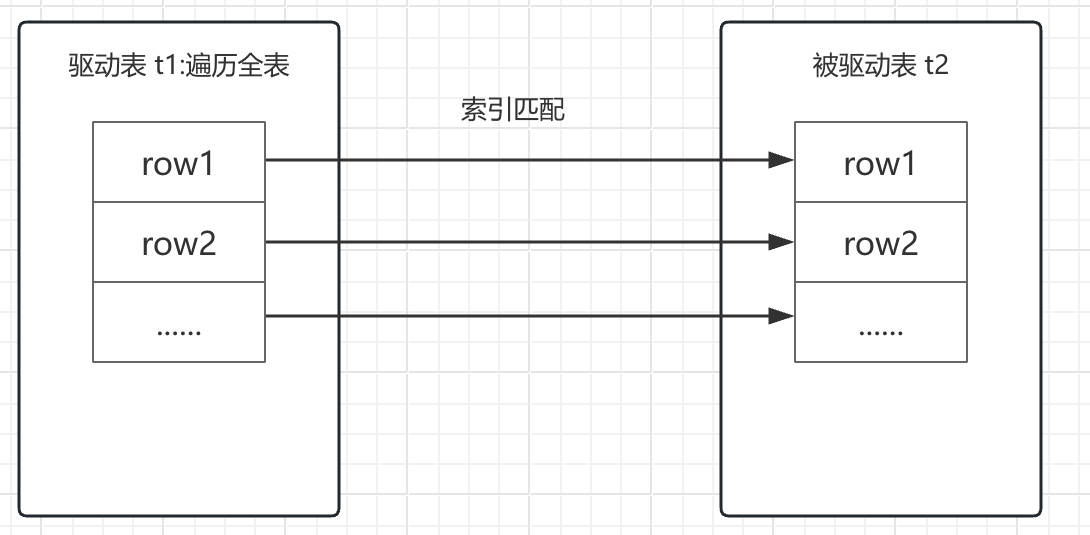
驱动表中的每一行记录,都可以通过被驱动表的索引列,进行索引查找(与关联列有关,可以是主键,也可以是二级索引),这瞬间就解决了被驱动表被扫描的问题。其本质,和单表查询中,通过建立合适索引的方式进行优化,是不是很相似。哪怕驱动表再大,如果索引列每个键值对应的数据量不大,那么索引查找速度依然可以快到起飞,这算法就叫 Index Nested-Loop Join。
先前咱两个测试表中,a列和b列数据是一样的,a列有索引,b列无索引,所以,咱将测试SQL变通一下
select * from t1 join t2 on t1.b=t2.b;
# 替换为
select * from t1 join t2 on t1.b=t2.a;
执行计划:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>explain select * from t1 join t2 on t1.b=t2.a\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t1
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 1000
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using where
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t2
partitions: NULL
type: ref
possible_keys: idx_a
key: idx_a
key_len: 5
ref: db1.t1.b
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
执行速度:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>select * from t1 join t2 on t1.b=t2.a;
......
+------+------+------+------+------+------+
500 rows in set (0.01 sec)
你是不是在疑惑,看这执行速度,和Hash Join差别也不大,那是因为咱的被驱动表t2数据量太少,随着测试数据量的增大,差距会越来越明显。
四、优化思路
前面的测试SQL,相对来讲,简化的有点过于简单了,实际应用中,必然会有一大堆查询条件跟在其后,那这一堆查询条件,在进行SQL优化时,会不会对你造成干扰呢?
1、初始SQL
测试SQL做个变化,让其他稍微贴近实际情况:
select *
from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.b
where
t1.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
and t2.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30);
执行计划:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>explain select *
-> from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.b
-> where
-> t1.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
-> and t2.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t1
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 1000
filtered: 50.00
Extra: Using where
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t2
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 100345
filtered: 5.00
Extra: Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop)
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
从上面的执行计划可以看到,t1表较小为驱动表,t2表较大为被驱动表。咱一步一步分析,暂时剔除t2表,先看t1表是否有优化的空间,其现在是全表扫描,并通过t1.c列进行数据过滤。单表查询,如果查询条件列有索引,必然会加快查询速度对吧。
2、SQL优化1
t1表中,a、b、c列数据是一样的,a列有索引,所以咱不额外创建索引了,直接使用a列替代c列,重写测试SQL:
select *
from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.b
where
t1.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
and t2.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30);
查看新的执行计划:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>explain select *
-> from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.b
-> where
-> t1.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
-> and t2.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t1
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: idx_a
key: idx_a
key_len: 5
ref: NULL
rows: 5
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using index condition
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t2
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 100345
filtered: 5.00
Extra: Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop)
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
t1表从原先的全表扫描,变成了索引查找,预估读取的数据行,也从原来的1000行变成了5行,优化效果明显。此时,再看看t2表,因为关联列t2.b没有索引,查询列t2.c也没有索引,所以t2表是扫描一次后,通过Block Nested-Loop Join算法与Join Buffer中的数据进行匹配。
在前面讲解Index Nested-Loop Join时,咱知道,如果关联列 t2.b 有索引,就会使用Index Nested-Loop Join算法进行数据匹配,那,如果关联列没索引,但是查询过滤列 t2.c 有索引,会是怎样的?
3、SQL优化2
同样的,咱用 t2.a 列替代 t2.c 列,重写测试SQL:
select *
from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.b
where
t1.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
and t2.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30);
执行计划:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>explain select *
-> from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.b
-> where
-> t1.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
-> and t2.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t1
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: idx_a
key: idx_a
key_len: 5
ref: NULL
rows: 5
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using index condition
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t2
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: idx_a
key: idx_a
key_len: 5
ref: NULL
rows: 5
filtered: 10.00
Extra: Using index condition; Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop)
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
与前面的执行计划对比发现,其依然是使用Block Nested-Loop Join算法,只不过原先t2表,从全表扫描,变成了通过 t2.a 列索引,一次性查找出全部数据后,再与Join Buffer中t1表的结果集进行匹配,如果 t2.a 列根据查询条件过滤出来的数据,足够少,这也不失为一个较好的优化思路。
4、SQL优化3
当然了,如果关联列有索引,查询列没索引,你已经知道了是使用Index Nested-Loop Join算法,继续重写测试SQL:
select *
from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.a
where
t1.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
and t2.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30);
执行计划:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>explain select *
-> from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.a
-> where
-> t1.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
-> and t2.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t1
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: idx_a
key: idx_a
key_len: 5
ref: NULL
rows: 5
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using index condition; Using where
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t2
partitions: NULL
type: ref
possible_keys: idx_a
key: idx_a
key_len: 5
ref: db1.t1.b
rows: 1
filtered: 50.00
Extra: Using where
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
被驱动表关联列有索引,查询列无索引,使用Index Nested-Loop Join算法。
5、疑问
如果t2表中,关联列和查询列,都有索引,他会怎么选?为了更好的比较,咱给 t2.c 列创建一个索引,并对 t2.a 列的数据进行适当的调整。
# 添加c列索引
alter table t2 add index idx_c(c);
# 调整t2表a列数据,a列查询条件中的值,每个值对应的数据量为4000
update t2 set a=a%50;
# 消除表碎片,避免被其干扰
alter table t2 engine=innodb;
# 驱动表传过来的键值,每个键值对应的数据为4000行
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>select a,count(a) cnt
-> from t2
-> where a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
-> group by a;
+------+------+
| a | cnt |
+------+------+
| 6 | 4000 |
| 12 | 4000 |
| 18 | 4000 |
| 24 | 4000 |
| 30 | 4000 |
+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.01 sec)
# 总共符合条件的数据,5行
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>select * from t2 where c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30);
+----+------+------+------+
| id | a | b | c |
+----+------+------+------+
| 3 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 6 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 9 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| 12 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| 15 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
+----+------+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.01 sec)
重写测试SQL:
select *
from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.a
where
t1.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
and t2.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30);
执行计划:
[5.7.37-log localhost:mysql.sock]>explain select *
-> from t1 join t2 on t1.b = t2.a
-> where
-> t1.a in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)
-> and t2.c in (6, 12, 18, 24, 30)\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t1
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: idx_a
key: idx_a
key_len: 5
ref: NULL
rows: 5
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using index condition
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: t2
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: idx_a,idx_c
key: idx_c
key_len: 5
ref: NULL
rows: 5
filtered: 4.55
Extra: Using index condition; Using where; Using join buffer (Block Nested Loop)
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
由此可见,Block Nested-Loop Join (Hash Join)与 Index Nested-Loop Join 对比,并没有哪一种算法更优一说,只要其整体成本比另一种低,那他就是最合适的。当然了,前面所有例子,都是只有2个表关联,对于3表及以上的关联SQL而言,如果你把前2个表的关联结果,当成一个新的驱动表看待,那么所有后面的表关联,是不是都只需分析两表关联的情况即可。
五、最后
至此,对于想学习SQL优化的你,功力是不是又有长进了。如果你还有其他疑问,可以写在评论区,咱后面再继续探讨。另,如果上述内容你对你有帮助,不要吝啬你的小手,点赞收藏转发,动起来。











