一、认识Caffeine
1、Caffeine是什么?
Caffeine是一个基于Java8开发的提供了近乎最佳命中率的高性能的缓存库, 也是SpringBoot内置的本地缓存实现。
2、Caffeine提供了灵活的构造器去创建一个拥有下列特性的缓存:
- 自动加载条目到缓存中,可选异步方式
- 可以基于大小剔除
- 可以设置过期时间,时间可以从上次访问或上次写入开始计算
- 异步刷新
- keys自动包装在弱引用中
- values自动包装在弱引用或软引用中
- 条目剔除通知
- 缓存访问统计
3、核心类和参数
核心工具类:Caffeine是创建高性能缓存的基类。
核心参数:
maximumSize:缓存最大值
maximumWeight:缓存最大权重,权重和最大值不能同时设置
initialCapacity:缓存初始容量
expireAfterWriteNanos:在写入多少纳秒没更新后过期
expireAfterAccessNanos:在访问多少纳秒没更新后过期
refreshAfterWriteNanos:写入多少纳秒没更新后更新
二、数据加载
Caffeine提供了四种缓存添加策略
1、手动加载
public static void demo() {
Cache<String, String> cache =
Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterAccess(Duration.ofMinutes(1))
.maximumSize(100)
.recordStats()
.build();
// 插入数据
cache.put("a", "a");
// 查询某个key,如果没有返回空
String a = cache.getIfPresent("a");
System.out.println(a);
// 查找缓存,如果缓存不存在则生成缓存元素, 如果无法生成则返回null
String b = cache.get("b", k -> {
System.out.println("begin query ..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("end query ...");
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
});
System.out.println(b);
// 移除一个缓存元素
cache.invalidate("a");
}
2、自动加载
public static void demo() {
LoadingCache<String, String> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build(new CacheLoader() {
@Nullable
@Override
public Object load(@NonNull Object key) throws Exception {
return createExpensiveValue();
}
@Override
public @NonNull Map loadAll(@NonNull Iterable keys) throws Exception {
if (keys == null) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Object key : keys) {
map.put((String) key, createExpensiveValue());
}
return map;
}
});
// 查找缓存,如果缓存不存在则生成缓存元素, 如果无法生成则返回null
String a = loadingCache.get("a");
System.out.println(a);
// 批量查找缓存,如果缓存不存在则生成缓存元素
Set<String> keys = new HashSet<>();
keys.add("a");
keys.add("b");
Map<String, String> allValues = loadingCache.getAll(keys);
System.out.println(allValues);
}
private static String createExpensiveValue() {
{
System.out.println("begin query ..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("end query ...");
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
}
一个LoadingCache是Cache附加一个CacheLoader能力之后的缓存实现。
getAll方法中,将会对每个key调用一次CacheLoader.load来生成元素,当批量查询效率更高的时候,你可以自定义loadAll方法实现。
3、手动异步加载
public static void demo() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
AsyncCache<String,String> asyncCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100)
.buildAsync();
// 添加或者更新一个缓存元素
asyncCache.put("a",CompletableFuture.completedFuture("a"));
// 查找一个缓存元素, 没有查找到的时候返回null
CompletableFuture<String> a = asyncCache.getIfPresent("a");
System.out.println(a.get());
// 查找缓存元素,如果不存在,则异步生成
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = asyncCache.get("b", k ->createExpensiveValue("b"));
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
// 移除一个缓存元素
asyncCache.synchronous().invalidate("a");
System.out.println(asyncCache.getIfPresent("a"));
}
private static String createExpensiveValue(String key) {
{
System.out.println("begin query ..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("end query ...");
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
}
一个`AsyncCache`是 `Cache`的一个变体,`AsyncCache`提供了在 Executor上生成缓存元素并返回 CompletableFuture的能力。这给出了在当前流行的响应式编程模型中利用缓存的能力。
synchronous()方法给 Cache提供了阻塞直到异步缓存生成完毕的能力。
异步缓存默认的线程池实现是 ForkJoinPool.commonPool() ,你也可以通过覆盖并实现 `Caffeine.executor(Executor)`方法来自定义你的线程池选择。
4、自动异步加载
public static void demo() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
AsyncLoadingCache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10_000)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
// 你可以选择: 去异步的封装一段同步操作来生成缓存元素
//.buildAsync(key -> createExpensiveValue(key));
// 你也可以选择: 构建一个异步缓存元素操作并返回一个future
.buildAsync((key, executor) ->createExpensiveValueAsync(key, executor));
// 查找缓存元素,如果其不存在,将会异步进行生成
CompletableFuture<String> a = cache.get("a");
System.out.println(a.get());
// 批量查找缓存元素,如果其不存在,将会异步进行生成
Set<String> keys = new HashSet<>();
keys.add("a");
keys.add("b");
CompletableFuture<Map<String, String>> values = cache.getAll(keys);
System.out.println(values.get());
}
private static String createExpensiveValue(String key) {
{
System.out.println("begin query ..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("end query ...");
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
}
private static CompletableFuture<String> createExpensiveValueAsync(String key, Executor executor) {
{
System.out.println("begin query ..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
executor.execute(()-> System.out.println("async create value...."));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("end query ...");
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
}
一个 AsyncLoadingCache是一个 AsyncCache 加上 AsyncCacheLoader能力的实现。
在需要同步的方式去生成缓存元素的时候,CacheLoader是合适的选择。而在异步生成缓存的场景下, AsyncCacheLoader则是更合适的选择并且它会返回一个 CompletableFuture。
三、驱除策略
Caffeine 提供了三种驱逐策略,分别是基于容量,基于时间和基于引用三种类型;还提供了手动移除方法和监听器。
1、基于容量
// 基于缓存容量大小,缓存中个数进行驱逐
Cache<String, String> cache =
Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100)
.recordStats()
.build();
// 基于缓存的权重进行驱逐
AsyncCache<String,String> asyncCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumWeight(10)
.buildAsync();
2、基于时间
// 基于固定时间
Cache<Object, Object> cache =
Caffeine.newBuilder()
//距离上次访问后一分钟删除
.expireAfterAccess(Duration.ofMinutes(1))
.recordStats()
.build();
Cache<Object, Object> cache =
Caffeine.newBuilder()
// 距离上次写入一分钟后删除
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(1))
.recordStats()
.build();
// 基于不同的过期驱逐策略
Cache<String, String> expire =
Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfter(new Expiry<String, String>() {
@Override
public long expireAfterCreate(@NonNull String key, @NonNull String value, long currentTime) {
return LocalDateTime.now().plusMinutes(5).getSecond();
}
@Override
public long expireAfterUpdate(@NonNull String key, @NonNull String value, long currentTime, @NonNegative long currentDuration) {
return currentDuration;
}
@Override
public long expireAfterRead(@NonNull String key, @NonNull String value, long currentTime, @NonNegative long currentDuration) {
return currentDuration;
}
})
.recordStats()
.build();
Caffeine提供了三种方法进行基于时间的驱逐:
expireAfterAccess(long, TimeUnit):一个值在最近一次访问后,一段时间没访问时被淘汰。expireAfterWrite(long, TimeUnit):一个值在初次创建或最近一次更新后,一段时间后被淘汰。expireAfter(Expiry):一个值将会在指定的时间后被认定为过期项。
3、基于引用
java对象引用汇总表:
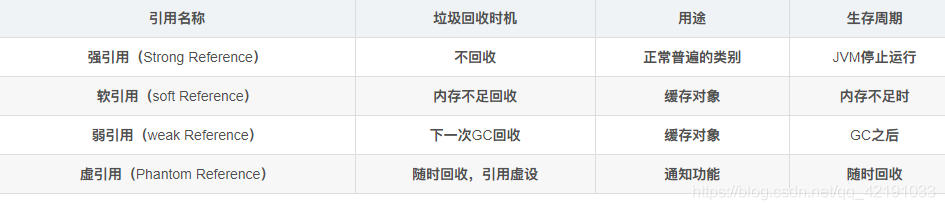
// 当key和缓存元素都不再存在其他强引用的时候驱逐
LoadingCache<Object, Object> weak = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.weakKeys()
.weakValues()
.build(k ->createExpensiveValue());
// 当进行GC的时候进行驱逐
LoadingCache<Object, Object> soft = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.softValues()
.build(k ->createExpensiveValue());
weakKeys:使用弱引用存储key时,当没有其他的强引用时,则会被垃圾回收器回收。
weakValues:使用弱引用存储value时,当没有其他的强引用时,则会被垃圾回收器回收。
softValues:使用软引用存储key时,当没有其他的强引用时,内存不足时会被回收。
4、手动移除
Cache<Object, Object> cache =
Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(1))
.recordStats()
.build();
// 单个删除
cache.invalidate("a");
// 批量删除
Set<String> keys = new HashSet<>();
keys.add("a");
keys.add("b");
cache.invalidateAll(keys);
// 失效所有key
cache.invalidateAll();
任何时候都可以手动删除,不用等到驱逐策略生效。
5、移除监听器
Cache<Object, Object> cache =
Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofMinutes(1))
.recordStats()
.evictionListener(new RemovalListener<Object, Object>() {
@Override
public void onRemoval(@Nullable Object key, @Nullable Object value, @NonNull RemovalCause cause) {
System.out.println("element evict cause" + cause.name());
}
})
.removalListener(new RemovalListener<Object, Object>() {
@Override
public void onRemoval(@Nullable Object key, @Nullable Object value, @NonNull RemovalCause cause) {
System.out.println("element removed cause" + cause.name());
}
}).build();
你可以为你的缓存通过Caffeine.removalListener(RemovalListener)方法定义一个移除监听器在一个元素被移除的时候进行相应的操作。这些操作是使用 Executor异步执行的,其中默认的 Executor 实现是 ForkJoinPool.commonPool()并且可以通过覆盖Caffeine.executor(Executor)方法自定义线程池的实现。
注意:Caffeine.evictionListener(RemovalListener)。这个监听器将在 RemovalCause.wasEvicted()为 true 的时候被触发。
6、驱逐原因汇总
EXPLICIT:如果原因是这个,那么意味着数据被我们手动的remove掉了
REPLACED:就是替换了,也就是put数据的时候旧的数据被覆盖导致的移除
COLLECTED:这个有歧义点,其实就是收集,也就是垃圾回收导致的,一般是用弱引用或者软引用会导致这个情况
EXPIRED:数据过期,无需解释的原因。
SIZE:个数超过限制导致的移除
四、缓存统计
Caffeine通过使用Caffeine.recordStats()方法可以打开数据收集功能,可以帮助优化缓存使用。
// 缓存访问统计
CacheStats stats = cache.stats();
System.out.println("stats.hitCount():"+stats.hitCount());//命中次数
System.out.println("stats.hitRate():"+stats.hitRate());//缓存命中率
System.out.println("stats.missCount():"+stats.missCount());//未命中次数
System.out.println("stats.missRate():"+stats.missRate());//未命中率
System.out.println("stats.loadSuccessCount():"+stats.loadSuccessCount());//加载成功的次数
System.out.println("stats.loadFailureCount():"+stats.loadFailureCount());//加载失败的次数,返回null
System.out.println("stats.loadFailureRate():"+stats.loadFailureRate());//加载失败的百分比
System.out.println("stats.totalLoadTime():"+stats.totalLoadTime());//总加载时间,单位ns
System.out.println("stats.evictionCount():"+stats.evictionCount());//驱逐次数
System.out.println("stats.evictionWeight():"+stats.evictionWeight());//驱逐的weight值总和
System.out.println("stats.requestCount():"+stats.requestCount());//请求次数
System.out.println("stats.averageLoadPenalty():"+stats.averageLoadPenalty());//单次load平均耗时










