函数式编程简介
常见应用场景
1、ES6中的map、filter、reduce等函数
[1,2,3,4,5].map(x => x * 2).filter(x => x > 5).reduce((p,n) => p + n);2、React类组件 -> 函数式组件+hooks、Vue3中的组合式API
3、RxJS、Lodash和Ramda等JS库
4、中间件/插件,如Redux中的applyMiddleware中间件实现
const store = applyMiddleware(...middlewares)(createStore)(reducer, initialState)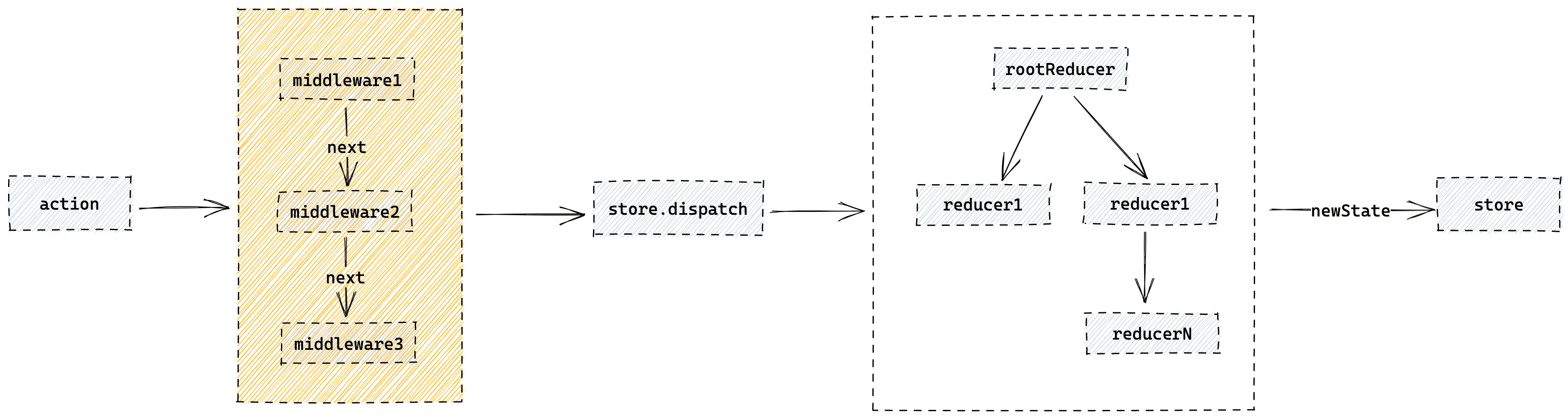
什么是函数式编程
函数式编程是一种编程范式,它将程序抽象为函数和数据结构,通过函数调用来实现程序的功能,并且函数可以作为参数传递给其他函数。
在 JavaScript 中,函数式编程可以实现面向对象编程的一些功能,比如抽象、封装、继承和多态等。
它还可以使用高阶函数、柯里化、组合和延迟计算来实现函数式编程的功能。
函数式编程有哪些特性
函数是「一等公民」
- 函数可以当做参数传递给其他函数,也可以作为函数的返回值返回(高阶函数)。
惰性执行
- 惰性执行是指在代码中的某些函数调用,只有在它们的返回值被使用时才会被执行。
- 它利用了延迟计算的技术,使得函数只在被调用时才会执行,而不是在编写代码时就被执行。
- 这样可以提高性能,因为不需要无用的计算。
无副作用(纯函数)
- 函数的执行不会改变程序的外部状态,也就是说函数的执行不会影响程序的其他部分。
- 因为它只是单纯的计算结果,而不会产生其他的副作用。
常见函数式概念
柯里化-currying
柯里化函数是把接受多个参数的函数变换成接受一个单一参数(最初函数的第一个参数)的函数,并且返回接受余下的参数而且返回结果的新函数的技术。
函数表达:f(a, b, c) => f(a)(b)(c)
简单实现(有兴趣的同学可以研究下Lodash和Ramda库中的实现)
// 函数柯里化
function curry(fn, args){
args = args || []
return function(...params){
let _args = [...args, ...params]
if(_args.length < fn.length){
return curry(fn, _args)
}
return fn.apply(this, _args)
}
}
function sum(a, b, c){
return a+b+c
}
// 自由组合参数
const currySum = curry(sum)
console.log(currySum(1)(2)(3)) //6
console.log(currySum(1)(2,3)) //6
console.log(currySum(1,2)(3)) //6管道-pipe
管道pipe函数是一个高阶函数,它接受一系列函数作为参数,将函数串联起来,一步步将上一步的输出作为下一步的输入,这样可以更加高效地处理复杂的业务逻辑。
函数表达:pipe(f, g, t) => x => t(g(f(x)),进一步结合curry可以实现pipe(f)(g)(t) => x => t(g(f(x))
借助reduce简单实现,支持异步和非异步函数
export const pipe: any =
(...fns: Promise<Function>[]) =>
(input: any) =>
fns.reduce((chain: Promise<Function>, func: Function | Promise<Function> | any) => chain.then(func), Promise.resolve(input));组合-compose
组合compose指的是将多个函数组合成一个函数,这样一个函数的输出就可以作为另一个函数的输入,从而实现多个函数的链式调用。
组合compose可以提高代码的可读性和可维护性,减少重复代码的出现,更加便捷的实现函数的复用。
函数表达:compose(f, g, t) => x => f(g(t(x)),进一步结合curry可以实现compose(f)(g)(t) => x => f(g(t(x))
借助reduceRight简单实现,和pipe的区别只是运算顺序不同
export const compose: any =
(...fns: Promise<Function>[]) =>
(input: any) =>
fns.reduceRight((chain: Promise<Function>, func: Function | Promise<Function> | any) => chain.then(func), Promise.resolve(input));函数式编程实践
需求背景介绍
AgileBI在线报表是一款报表应用工具:易学易用,零代码,通过简单拖拽操作,制作中国式复杂报表,轻松实现报表的多样展示、交互分析、数据导出等需求, 在线体验
已有功能:在线报表中的每个单元格都可以配置相关的属性:比如扩展方向、父格、单元格格式、过滤条件、条件属性等
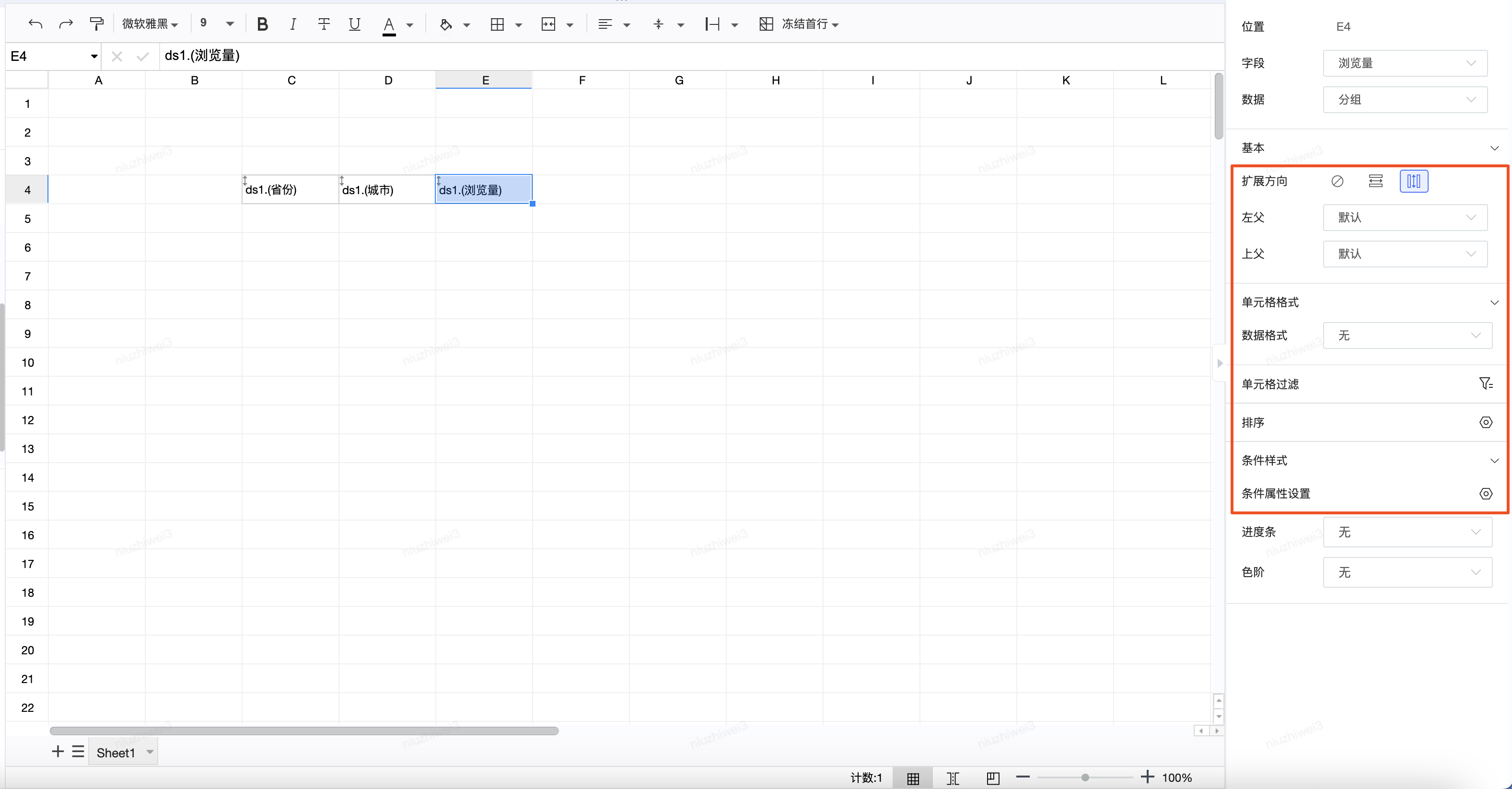
新增需求:需要支持批量设置单元格,其中【文本类型】单元格支持扩展方向、父格的设置;【字段类型】、【公示类型】单元格支持所有配置;
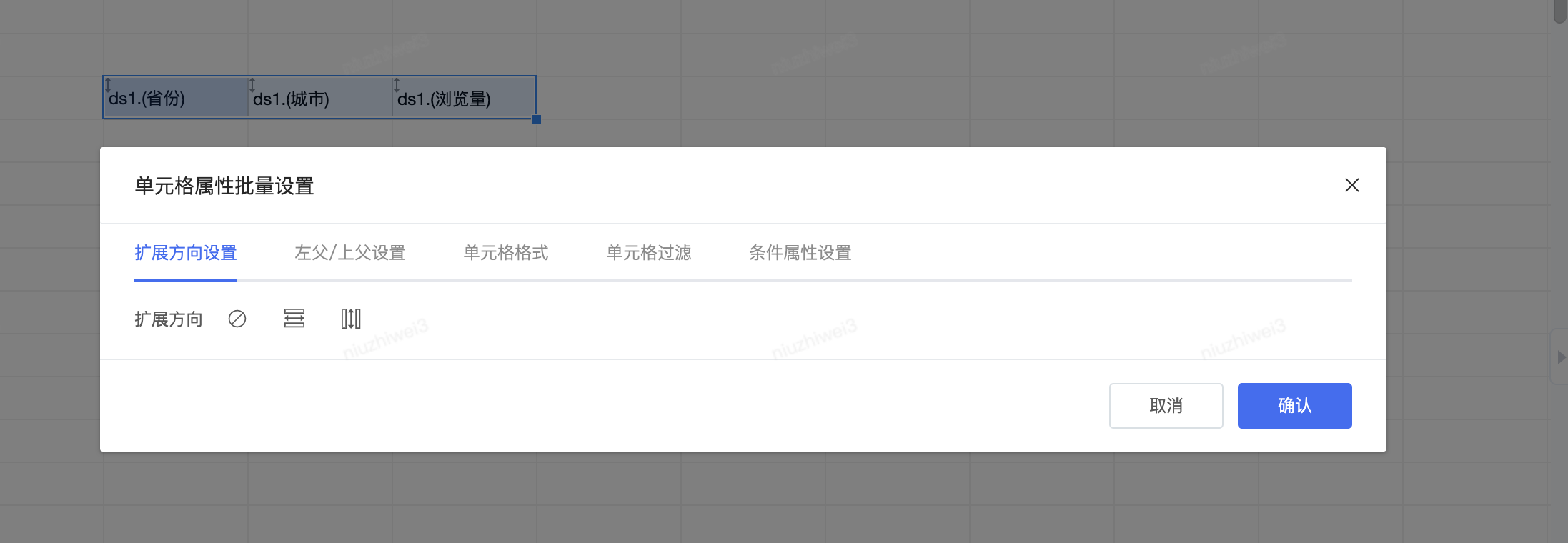
大致设计思路
- 获取当前批量设置中,所有的配置项信息
- 为每个配置项设计一个处理器(高阶函数):主要处理【批量设置的配置信息】和【当前单元格的配置信息】合并或替换逻辑
- 通过管道的方式,加工每个单元格所有的配置项信息
核心实现
- pipe函数
private pipe = (...args: any) => {
return (result: any, config?: any) => {
return args.reduce((acc: any, fn: any) => fn(acc, config), result);
};
};- 高阶函数处理每个配置项
// 扩展方向替换
private handleExpand(expandConf: string) {
return (conf: any) => {
if (expandConf) {
conf.expandDirection = expandConf;
}
return conf;
};
}
// 父行/父列替换
private handleParentCell(columnParentCell: any, rowParentCell: any) {
return (conf: any) => {
if (columnParentCell?.parentSelectType) {
conf.columnParentCell = columnParentCell;
}
if (rowParentCell?.parentSelectType) {
conf.rowParentCell = rowParentCell;
}
return conf;
};
}
// 条件属性追加
private handleCondition(conditionBatchConf: any) {
return (conf: any) => {
conf.conditionConf = this.mergeCondition(conf?.conditionConf || [], conditionBatchConf);
return conf;
};
}
// 批量修改
private mergeCondition(c1: any, c2: any) {
for (let j = 0; j < c1.length; j++) {
// 批量删除
if (
c1[j]?.batchFlag &&
this.batchConf.conditionConf?.find((item: any) => item.uuid === c1[j]?.uuid) &&
!c2.find((item: any) => item.uuid === c1[j]?.uuid)
) {
c1.splice(j, 1);
}
}
for (let j = 0; j < c1.length; j++) {
for (let i = 0; i < c2.length; i++) {
// 如果字段已存在则替换
if (c2[i]?.uuid === c1[j]?.uuid) {
c1.splice(j, 1);
}
}
}
return [...c1, ...c2];
}
//...- 组合函数,获取每个单元格的最终配置信息
//...
let handles: Array<any> = [];
if (cell?.dataConf?.cellType === "文本") {
handles = [
this.handleExpand(conf.expandDirection),
this.handleParentCell(conf.columnParentCell, conf.rowParentCell)
];
} else if (cell?.dataConf?.cellType === "字段" || cell?.dataConf?.cellType === "公式") {
handles = [
this.handleExpand(conf.expandDirection),
this.handleParentCell(conf.columnParentCell, conf.rowParentCell),
this.handleFormat(conf.dataFormatConf),
this.handleFilter(conf.cellFilterConf),
this.handleCondition(conf.conditionConf)
];
}
if (handles.length > 0) {
const mergeConf = this.pipe(...handles)(JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(cell.dataConf)));
//...
}总结
- 函数式编程可以可提高代码的可重用性,减少重复代码的开发时间;
- 函数式编程可以提高代码的可读性,使得代码更容易理解和调试;
- 函数式编程可以更容易实现函数组合,以帮助提高可维护性;
- 组合优于继承;











