笔者由于工作中需要用到图数据库,所以花2小时研究了下Janus Graph这个开源项目,下面是一些学习心得,如果后面使用有更多启发再更新,如有错误,欢迎错误。
学习一门技术最标准的方式是从官网入门:https : //docs.janusgraph.org/
然后搞清楚以下问题即可:
- 是什么?为什么出现?
- 基本原理
- 怎么使用
- 再深刻理解原理
1.JanusGraph是什么
本质问题是图数据库是什么?
JanusGraph预先支持当需要的存储和计算能力超过了单台计算机所能提供的范围的图处理。包括对图数据进行实时遍历和分析查询,这是JanusGraph的基本优势。
关键词是:图数据,实时遍历,实时查询和分析。
实际上,很多数据不再是关系型数据了,某些情况下,人的关系网络,物联网,物流,交通等。对这种数据进行查询就像对树进行深度或广度遍历,只是图多个包括树,更像是森林。
下面是笔者绘制的Janus图的基本数据组成:https ://docs.janusgraph.org/basics/schema/
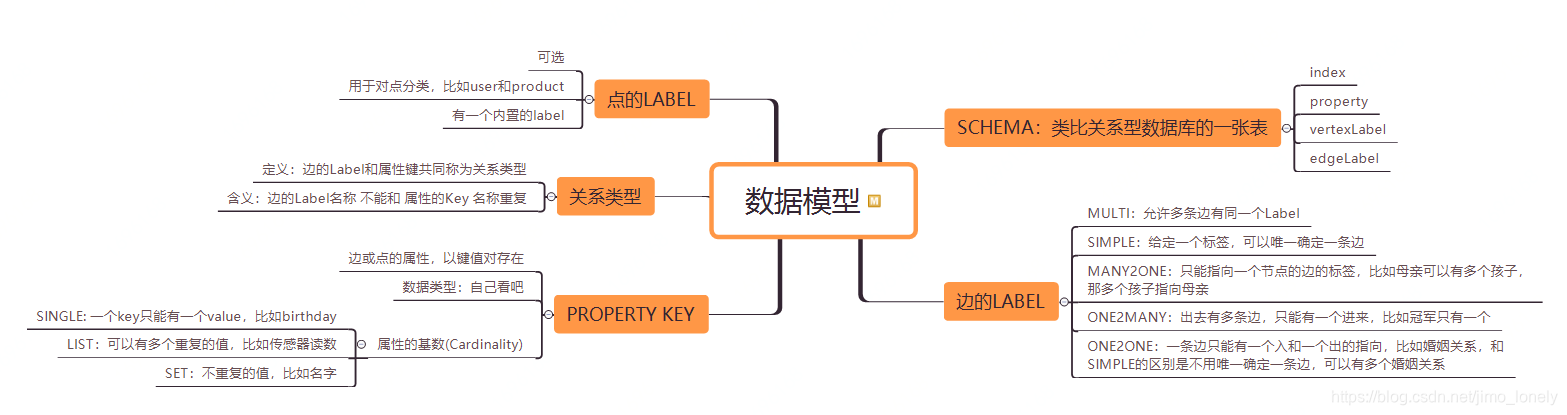
2.基本原理
2.1。存储
Janus支持的存储有
Apache Cassandra
Apache HBase
Oracle Berkeley DB Java Edition存储和索引是分开的:
Elasticsearch
Apache Solr
Apache Lucene以hbase为例:Janus只支持等值查询,将索引属性的值做一个哈希,然后分段存储在多个区域服务器中,这样可以避免查询热点。
2.2。部署场景
https://docs.janusgraph.org/basics/deployment/
当单独以Janus Server模式部署时,客户端与服务器进行交互可以选择:
- HTTP方式
- WebSocket方式
- 或者2者的组合
3.怎么使用
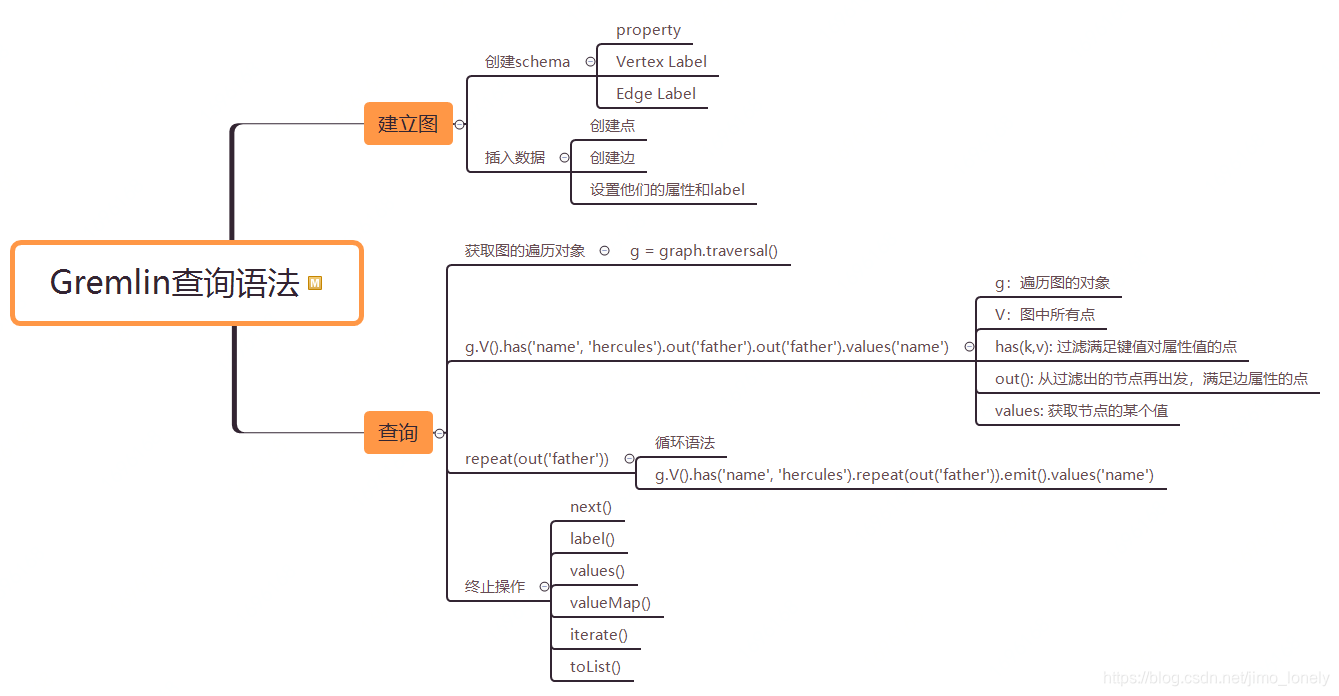
对图的操作,最连续的就是查询和分析,下面是一个demo项目。
演示
我们采用集成在应用里的方式,建一个java项目。
引入依赖
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<janusgraph.version>0.5.1</janusgraph.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.janusgraph/janusgraph-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.janusgraph</groupId>
<artifactId>janusgraph-core</artifactId>
<version>${janusgraph.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.janusgraph/janusgraph-berkeleyje -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.janusgraph</groupId>
<artifactId>janusgraph-berkeleyje</artifactId>
<version>${janusgraph.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.janusgraph</groupId>
<artifactId>janusgraph-driver</artifactId>
<version>${janusgraph.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.janusgraph/janusgraph-inmemory -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.janusgraph</groupId>
<artifactId>janusgraph-inmemory</artifactId>
<version>${janusgraph.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tinkerpop</groupId>
<artifactId>gremlin-driver</artifactId>
<version>3.4.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>建立图
- 选择图的存储方式:此处为了快速使用,我们基于内存创建
private static JanusGraph graph;
@BeforeAll
static void _1_create_graph_and_init_data() {
final PropertiesConfiguration configuration = getGanusConfiguration();
graph = JanusGraphFactory.open(configuration);
// management = graph.openManagement();
initSchema();
initData();
}
private static PropertiesConfiguration getGanusConfiguration() {
final PropertiesConfiguration p = new PropertiesConfiguration();
p.setProperty("storage.backend", "inmemory");
return p;
} - 初始化schema:就像建表一样,不过这里的结构是:点和边的label,属性keyValue
private static void initSchema() {
// final VertexLabel vHumanLabel = management.makeVertexLabel("v_human").make();
final PropertyKey pkName = graph.makePropertyKey("pk_name")
.dataType(String.class).cardinality(Cardinality.SET).make();
// 人这个点有一个属性是姓名
final VertexLabel vHumanLabel = graph.makeVertexLabel("v_human").make();
graph.addProperties(vHumanLabel, pkName);
// 婚姻这条边有一个属性是结婚年龄, 同时是一个无向边
final PropertyKey pkMarriedYear = graph.makePropertyKey("pk_married_year")
.dataType(Integer.class).cardinality(Cardinality.SINGLE).make();
final EdgeLabel eWifeLabel = graph.makeEdgeLabel("e_married")
/*.unidirected()*/.multiplicity(Multiplicity.ONE2ONE).make();
graph.addProperties(eWifeLabel, pkMarriedYear);
// 朋友关系,无向,多对多,有一个属性是好友关系强度
final PropertyKey pkTight = graph.makePropertyKey("pk_tight")
.dataType(Double.class).cardinality(Cardinality.SINGLE).make();
final EdgeLabel eFriendLabel = graph.makeEdgeLabel("e_friend")
/*.unidirected()*/.multiplicity(Multiplicity.MULTI).make();
graph.addProperties(eFriendLabel, pkTight);
}- 导入数据:这里插入3个点,3条关系
private static void initData() {
final String vHumanLabel = "v_human";
final String eMarriedLabel = "e_married";
final String eFriendLabel = "e_friend";
final String pkMarriedYear = "pk_married_year";
final String pkName = "pk_name";
final String pkTight = "pk_tight";
final Vertex vJimo = graph.addVertex(vHumanLabel);
vJimo.property(pkName, "Jimo");
final Vertex vLily = graph.addVertex(vHumanLabel);
vLily.property(pkName, "Lily");
final Vertex vHehe = graph.addVertex(vHumanLabel);
vHehe.property(pkName, "Hehe");
vJimo.addEdge(eMarriedLabel, vLily, pkMarriedYear, 10);
vJimo.addEdge(eFriendLabel, vLily, pkTight, 0.5);
vJimo.addEdge(eFriendLabel, vHehe, pkTight, 0.8);
// vHehe.addEdge(eFriendLabel, vJimo, pkTight, 0.8);
}查询测试
- 遍历所有点和边:
@Test
void _2_traversal_all() {
final GraphTraversalSource g = graph.traversal();
final List<Vertex> vertices = g.V().toList();
for (Vertex v : vertices) {
System.out.println(v.label() + ":" + v.property("pk_name"));
}
final List<Edge> edges = g.E().toList();
for (Edge e : edges) {
final Iterator<Property<Object>> properties = e.properties();
System.out.print(e.label() + ":");
while (properties.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(properties.next() + ",");
}
System.out.println();
}
}结果:
v_human:vp[pk_name->Jimo]
v_human:vp[pk_name->Lily]
v_human:vp[pk_name->Hehe]
e_married:p[pk_married_year->10],
e_friend:p[pk_tight->0.8],
e_friend:p[pk_tight->0.5],- 查询Jimo的朋友和老婆
@Test
void _3_query() {
final GraphTraversalSource g = graph.traversal();
final Vertex myWife = g.V().has("pk_name", "Jimo").out("e_married").next();
printVertex(myWife);
final List<Vertex> jimoFriends = g.V().has("pk_name", "Jimo").out("e_friend").toList();
System.out.println("Jimo friends:");
for (Vertex heheFriend : jimoFriends) {
printVertex(heheFriend);
}
}
private void printVertex(Vertex v) {
final Iterator<VertexProperty<Object>> ps = v.properties();
System.out.print(v.label() + ":");
while (ps.hasNext()) {
final VertexProperty<Object> property = ps.next();
System.out.print(property + ",");
}
System.out.println();
}结果:
v_human:vp[pk_name->Lily],
Jimo friends:
v_human:vp[pk_name->Lily],
v_human:vp[pk_name->Hehe],关闭图
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
graph.close();
}










