您好!
欢迎来到京东云开发者社区
登录
首页
博文
课程
大赛
工具
用户中心
开源
首页
博文
课程
大赛
工具
开源
更多
用户中心
开发者社区
>
博文
>
揭开烛龙平台卡顿监听的神秘面纱暨Android卡顿监听原理
分享
打开微信扫码分享
点击前往QQ分享
点击前往微博分享
点击复制链接
揭开烛龙平台卡顿监听的神秘面纱暨Android卡顿监听原理
京东ZERO团队
2021-01-07
IP归属:未知
1568浏览
Android
## 一、背景 在用户使用APP过程中,为保证应用的平滑性,每一帧渲染时间不能超过16ms,达到60帧每秒;如果UI渲染慢的话,就会发生丢帧,这样用户就会感觉到不连贯性,卡顿现象。卡顿容易被用户直观感受到,且造成卡顿的原因错综复杂,定位困难,很多平台都要对用户卡顿信息收集上报,用于卡顿问题的故障排查,指导APP流畅度优化 ## 二、原理 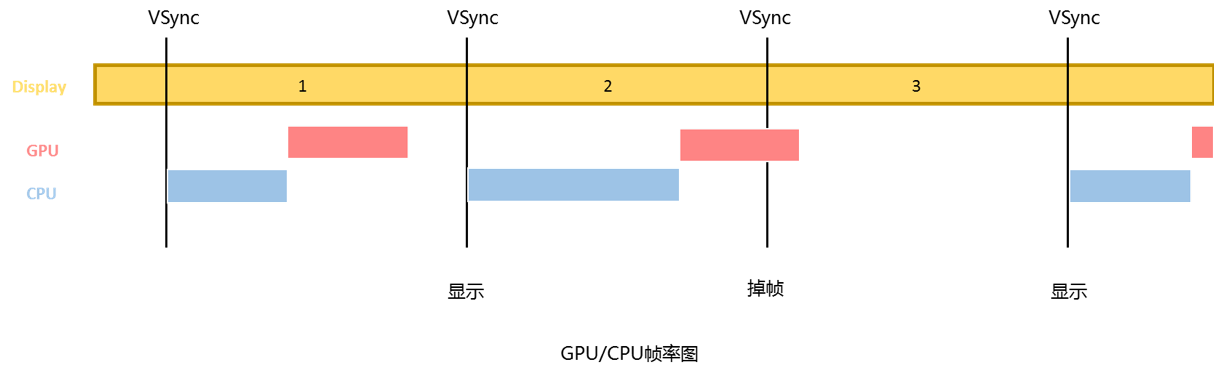 **CPU部分:** 逻辑的计算,例如:计算布局,解码图片,创建视图,绘制文本,计算好将要显示的内容转交给GPU; **GPU部分:** GPU开始变换,合成,渲染后将结果换到帧缓冲区,随后视频控制器从帧缓冲区中读取数据,经过一系列的转换后交给显示器进行显示; **帧率FPS:**Frames Per Second 的简称缩写,每秒传输帧数,FPS值越低越卡顿,所以这个值在一定程度上可以衡量应用在图像绘制渲染处理时的性能。60fps 最佳,一般我们的APP的FPS 只要保持在 50-60之间,用户体验都是比较流畅的。FPS=60时,1000/60≈16.7,大概16ms中,进行一次屏幕的刷新绘制; **VSync:** Vertical Synchronization的简称缩写,可以简单的理解成一个时间中断。例如,每16ms会有一个Vsync信号,那么系统在每次拿到Vsync信号时刷新屏幕。 从上图中看出,每两个VSync信号之间有时间间隔(16.7ms),在这个时间内,若CPU跟GPU进行界面渲染,计算跟绘制,让界面的帧率在1秒内达到60fps,则视觉上APP流畅度好,若在16ms内不能完成界面的渲染,计算跟绘制,就会产生丢帧的现象,丢帧就会造成应用卡顿现象。 ## 三、方案 通过原理我们可以很清楚的知道,如果能够统计系统绘制每一帧的起始时间,自然就能统计到目标视图渲染的耗时。如果制定相应的规则,便可以捕捉到整个应用的丢帧状况,进而做出改善。 Android系统就提供了这样的类,用于监听每一帧的绘制信息,这就是Choreographer。接下来从源码进度分析监听过程。 ## 四、源码分析 Choreographer提供了一个叫FrameCallback的回调接口,从官方定义可以知道,每渲染新的一帧,实现这个接口的类都会接收到回调。回调是在持有Choreographer的线程的Looper循环里完成的,调用的具体方法就是doFrame ```js /** * Implement this interface to receive a callback when a new display frame is * being rendered. The callback is invoked on the {@link Looper} thread to * which the {@link Choreographer} is attached. */ public interface FrameCallback { /** * Called when a new display frame is being rendered. * <p> * This method provides the time in nanoseconds when the frame started being rendered. * The frame time provides a stable time base for synchronizing animations * and drawing. It should be used instead of {@link SystemClock#uptimeMillis()} * or {@link System#nanoTime()} for animations and drawing in the UI. Using the frame * time helps to reduce inter-frame jitter because the frame time is fixed at the time * the frame was scheduled to start, regardless of when the animations or drawing * callback actually runs. All callbacks that run as part of rendering a frame will * observe the same frame time so using the frame time also helps to synchronize effects * that are performed by different callbacks. * </p><p> * Please note that the framework already takes care to process animations and * drawing using the frame time as a stable time base. Most applications should * not need to use the frame time information directly. * </p> * * @param frameTimeNanos The time in nanoseconds when the frame started being rendered, * in the {@link System#nanoTime()} timebase. Divide this value by {@code 1000000} * to convert it to the {@link SystemClock#uptimeMillis()} time base. */ public void doFrame(long frameTimeNanos); } ``` 有了每一帧渲染时的回调接口,系统只需要在相邻两帧之间发消息,就可以统计出渲染时长,通过跟标准帧率(16.7ms/帧),卡顿情况就一目了然了。为了方便用户调用,Choreographer类提供了postFrameCallback\postFrameCallbackDelayed方法。 ```js /** * Posts a frame callback to run on the next frame. * <p> * The callback runs once then is automatically removed. * </p> * * @param callback The frame callback to run during the next frame. * * @see #postFrameCallbackDelayed * @see #removeFrameCallback */ public void postFrameCallback(FrameCallback callback) { postFrameCallbackDelayed(callback, 0); } /** * Posts a frame callback to run on the next frame after the specified delay. * <p> * The callback runs once then is automatically removed. * </p> * * @param callback The frame callback to run during the next frame. * @param delayMillis The delay time in milliseconds. * * @see #postFrameCallback * @see #removeFrameCallback */ public void postFrameCallbackDelayed(FrameCallback callback, long delayMillis) { if (callback == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("callback must not be null"); } postCallbackDelayedInternal(CALLBACK_ANIMATION, callback, FRAME_CALLBACK_TOKEN, delayMillis); } ``` 这俩方法是兄弟俩,都是把FrameCallback抛到下一帧,区别在于后者有延时。无论如何最终都会走postFrameCallbackDelayed方法,该方法内部调用了postCallbackDelayedInternal方法,该方法的逻辑如下: ```js private void postCallbackDelayedInternal(int callbackType, Object action, Object token, long delayMillis) { synchronized (mLock) { final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); final long dueTime = now + delayMillis; mCallbackQueues[callbackType].addCallbackLocked(dueTime, action, token); // 代码1 if (dueTime <= now) { // 代码2 scheduleFrameLocked(now); } else { Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_DO_SCHEDULE_CALLBACK, action); msg.arg1 = callbackType; msg.setAsynchronous(true); mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, dueTime); } } } ``` action就是上面传入的callback,代码1处对回调做了存储,追踪代码会发现其实是存在了一个叫CallbackRecord的类中,然后CallbackRecord作为链表的一个节点存储。 ```js public void addCallbackLocked(long dueTime, Object action, Object token) { CallbackRecord callback = obtainCallbackLocked(dueTime, action, token); CallbackRecord entry = mHead; if (entry == null) { mHead = callback; return; } if (dueTime < entry.dueTime) { callback.next = entry; mHead = callback; return; } while (entry.next != null) { if (dueTime < entry.next.dueTime) { callback.next = entry.next; break; } entry = entry.next; } entry.next = callback; } ``` 回归到postCallbackDelayedInternal方法的代码2,由于我们以非延时执行逻辑为主线,系统会执行scheduleFrameLocked方法: ```js private void scheduleFrameLocked(long now) { if (!mFrameScheduled) { mFrameScheduled = true; if (USE_VSYNC) { if (DEBUG_FRAMES) { Log.d(TAG, "Scheduling next frame on vsync."); } // If running on the Looper thread, then schedule the vsync immediately, // otherwise post a message to schedule the vsync from the UI thread // as soon as possible. if (isRunningOnLooperThreadLocked()) { scheduleVsyncLocked(); } else { Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_DO_SCHEDULE_VSYNC); msg.setAsynchronous(true); mHandler.sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(msg); } } else { final long nextFrameTime = Math.max( mLastFrameTimeNanos / TimeUtils.NANOS_PER_MS + sFrameDelay, now); if (DEBUG_FRAMES) { Log.d(TAG, "Scheduling next frame in " + (nextFrameTime - now) + " ms."); } Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_DO_FRAME); msg.setAsynchronous(true); mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, nextFrameTime); } } } ``` 系统根据是否使用VSYNC垂直同步信号,判断是否借助VSYNC信号进行渲染。这里分析VSYNC信号的情况,系统最终都会调用scheduleVsyncLocked方法,并将DisplayEventReceiver的引用传递给native层。 ```js /** * Schedules a single vertical sync pulse to be delivered when the next * display frame begins. */ public void scheduleVsync() { if (mReceiverPtr == 0) { Log.w(TAG, "Attempted to schedule a vertical sync pulse but the display event " + "receiver has already been disposed."); } else { nativeScheduleVsync(mReceiverPtr); } } ``` 注意该方法的定义,计划在下一个显示帧开始时传递单个垂直同步脉冲。也就是说,下一帧开始时,才会给当前帧发送一个垂直同步脉冲信号VSYN,相邻两帧的时间差值就是绘制时间。那么系统是如何把VSYNC回传的呢? 其实FrameDisplayEventReceiver是DisplayEventReceiver派生类,而且它实现了runnable接口,在构建DisplayEventReceiver实例时,就已经消息队列传递给native层。 ```js /** * Creates a display event receiver. * * @param looper The looper to use when invoking callbacks. * @param vsyncSource The source of the vsync tick. Must be on of the VSYNC_SOURCE_* values. */ public DisplayEventReceiver(Looper looper, int vsyncSource) { if (looper == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("looper must not be null"); } mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue(); mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference<DisplayEventReceiver>(this), mMessageQueue, vsyncSource); mCloseGuard.open("dispose"); } ``` 底层在开始下一帧时将VSYNC信号放到消息队列中,并通过dispatchVsync完成分发任务。 ```js // Called from native code. @SuppressWarnings("unused") private void dispatchVsync(long timestampNanos, int builtInDisplayId, int frame) { onVsync(timestampNanos, builtInDisplayId, frame); } ``` 这里完成了一次承接,最终由FrameDisplayEventReceiver的onVsync方法完成消息处理。 ```js private final class FrameDisplayEventReceiver extends DisplayEventReceiver implements Runnable { private boolean mHavePendingVsync; private long mTimestampNanos; private int mFrame; public FrameDisplayEventReceiver(Looper looper, int vsyncSource) { super(looper, vsyncSource); } @Override public void onVsync(long timestampNanos, int builtInDisplayId, int frame) { // Ignore vsync from secondary display. // This can be problematic because the call to scheduleVsync() is a one-shot. // We need to ensure that we will still receive the vsync from the primary // display which is the one we really care about. Ideally we should schedule // vsync for a particular display. // At this time Surface Flinger won't send us vsyncs for secondary displays // but that could change in the future so let's log a message to help us remember // that we need to fix this. if (builtInDisplayId != SurfaceControl.BUILT_IN_DISPLAY_ID_MAIN) { Log.d(TAG, "Received vsync from secondary display, but we don't support " + "this case yet. Choreographer needs a way to explicitly request " + "vsync for a specific display to ensure it doesn't lose track " + "of its scheduled vsync."); scheduleVsync(); return; } // Post the vsync event to the Handler. // The idea is to prevent incoming vsync events from completely starving // the message queue. If there are no messages in the queue with timestamps // earlier than the frame time, then the vsync event will be processed immediately. // Otherwise, messages that predate the vsync event will be handled first. long now = System.nanoTime(); if (timestampNanos > now) { Log.w(TAG, "Frame time is " + ((timestampNanos - now) * 0.000001f) + " ms in the future! Check that graphics HAL is generating vsync " + "timestamps using the correct timebase."); timestampNanos = now; } if (mHavePendingVsync) { Log.w(TAG, "Already have a pending vsync event. There should only be " + "one at a time."); } else { mHavePendingVsync = true; } mTimestampNanos = timestampNanos; mFrame = frame; Message msg = Message.obtain(mHandler, this); msg.setAsynchronous(true); mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, timestampNanos / TimeUtils.NANOS_PER_MS); } @Override public void run() { mHavePendingVsync = false; doFrame(mTimestampNanos, mFrame); } } ``` onVsync会过滤掉一次无效信号,然后通过FrameHandler将消息发送到自己的消息队列,并调用自己的run方法。 在run中执行了 doFrame(mTimestampNanos, mFrame)逻辑,将最新的时间戳传回。 ```js void doFrame(long frameTimeNanos, int frame) { final long startNanos; synchronized (mLock) { if (!mFrameScheduled) { return; // no work to do } ...... long intendedFrameTimeNanos = frameTimeNanos; startNanos = System.nanoTime(); final long jitterNanos = startNanos - frameTimeNanos; if (jitterNanos >= mFrameIntervalNanos) { // 代码1 final long skippedFrames = jitterNanos / mFrameIntervalNanos; if (skippedFrames >= SKIPPED_FRAME_WARNING_LIMIT) { Log.i(TAG, "Skipped " + skippedFrames + " frames! " + "The application may be doing too much work on its main thread."); } final long lastFrameOffset = jitterNanos % mFrameIntervalNanos; if (DEBUG_JANK) { Log.d(TAG, "Missed vsync by " + (jitterNanos * 0.000001f) + " ms " + "which is more than the frame interval of " + (mFrameIntervalNanos * 0.000001f) + " ms! " + "Skipping " + skippedFrames + " frames and setting frame " + "time to " + (lastFrameOffset * 0.000001f) + " ms in the past."); } frameTimeNanos = startNanos - lastFrameOffset; } if (frameTimeNanos < mLastFrameTimeNanos) { // 代码2 if (DEBUG_JANK) { Log.d(TAG, "Frame time appears to be going backwards. May be due to a " + "previously skipped frame. Waiting for next vsync."); } scheduleVsyncLocked(); return; } if (mFPSDivisor > 1) { long timeSinceVsync = frameTimeNanos - mLastFrameTimeNanos; if (timeSinceVsync < (mFrameIntervalNanos * mFPSDivisor) && timeSinceVsync > 0) { scheduleVsyncLocked(); return; } } mFrameInfo.setVsync(intendedFrameTimeNanos, frameTimeNanos); mFrameScheduled = false; mLastFrameTimeNanos = frameTimeNanos; // 代码3 } try { // 代码4 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "Choreographer#doFrame"); AnimationUtils.lockAnimationClock(frameTimeNanos / TimeUtils.NANOS_PER_MS); mFrameInfo.markInputHandlingStart(); doCallbacks(Choreographer.CALLBACK_INPUT, frameTimeNanos); mFrameInfo.markAnimationsStart(); doCallbacks(Choreographer.CALLBACK_ANIMATION, frameTimeNanos); mFrameInfo.markPerformTraversalsStart(); doCallbacks(Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, frameTimeNanos); doCallbacks(Choreographer.CALLBACK_COMMIT, frameTimeNanos); } finally { AnimationUtils.unlockAnimationClock(); Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW); } if (DEBUG_FRAMES) { final long endNanos = System.nanoTime(); Log.d(TAG, "Frame " + frame + ": Finished, took " + (endNanos - startNanos) * 0.000001f + " ms, latency " + (startNanos - frameTimeNanos) * 0.000001f + " ms."); } } ``` 代码1处,通过与标准单帧耗时进行比较,如果信号发出到执行至代码1的时间耗时超过标准帧间距,说明主线程任务量大,需要舍弃(long)(jitterNanos / mFrameIntervalNanos)帧,并且取余获得补偿系数,修正frameTimeNanos这个起始时间。这 就是所谓的“丢帧”。 代码2处,如果修正后的起始时间frameTimeNanos小于上一帧的起始时间mLastFrameTimeNanos,说明丢帧造成时间戳后移,只能等待下一次VSYNC信号。同时,调用scheduleVsyncLocked触发二次信号,return结束本次同步。 代码3处,对当前帧的起始时间做了保存,根据代码2处的返回终止可以知道,相邻两次frameTimeNanos和mLastFrameTimeNanos的差值可以很大,因为存在不保存frameTimeNanos的情况。 经过以上分析,我们可以明白,只要记录两次时间取差值,就可以监听页面卡顿了。那么如何实现自定义规则呢? 代码4的try方法连续调用了4次doCallbacks方法,分别传入不同的回调类型Input callback、Animation callback、Traversal callback、 Commit callback ```js /** * Callback type: Input callback. Runs first. * @hide */ public static final int CALLBACK_INPUT = 0; /** * Callback type: Animation callback. Runs before traversals. * @hide */ @TestApi public static final int CALLBACK_ANIMATION = 1; /** * Callback type: Traversal callback. Handles layout and draw. Runs * after all other asynchronous messages have been handled. * @hide */ public static final int CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL = 2; /** * Callback type: Commit callback. Handles post-draw operations for the frame. * Runs after traversal completes. The {@link #getFrameTime() frame time} reported * during this callback may be updated to reflect delays that occurred while * traversals were in progress in case heavy layout operations caused some frames * to be skipped. The frame time reported during this callback provides a better * estimate of the start time of the frame in which animations (and other updates * to the view hierarchy state) actually took effect. * @hide */ public static final int CALLBACK_COMMIT = 3; ``` doCallback方法分别对这四种类型处理,无论哪种类型最终都会调用CallbackRecord的run方法。代码如下: ```js /** * @param callbackType: Input callback、Animation callback、Traversal callback、 Commit callback */ void doCallbacks(int callbackType, long frameTimeNanos) { CallbackRecord callbacks; synchronized (mLock) { // We use "now" to determine when callbacks become due because it's possible // for earlier processing phases in a frame to post callbacks that should run // in a following phase, such as an input event that causes an animation to start. final long now = System.nanoTime(); callbacks = mCallbackQueues[callbackType].extractDueCallbacksLocked( now / TimeUtils.NANOS_PER_MS); if (callbacks == null) { return; } mCallbacksRunning = true; ... ... try { Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, CALLBACK_TRACE_TITLES[callbackType]); for (CallbackRecord c = callbacks; c != null; c = c.next) { if (DEBUG_FRAMES) { Log.d(TAG, "RunCallback: type=" + callbackType + ", action=" + c.action + ", token=" + c.token + ", latencyMillis=" + (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - c.dueTime)); } c.run(frameTimeNanos); // 代码1 } } finally { ...... } ``` 代码1处,调用了CallbackRecord的run方法,而CallbackRecord#run的具体实现如下: ```js private static final class CallbackRecord { public CallbackRecord next; public long dueTime; public Object action; // Runnable or FrameCallback public Object token; public void run(long frameTimeNanos) { if (token == FRAME_CALLBACK_TOKEN) { ((FrameCallback)action).doFrame(frameTimeNanos); } else { ((Runnable)action).run(); } } } ``` 其实是执行了FrameCallback#doFrame方法,终于回到了开头。我们只需要实现FrameCallback接口,并在合适的位置通过Choreographer.getInstance().postFrameCallback(this.mFrameCallback);将其抛出即可完成时间戳的统计,实现监听目的。 烛龙系统的性能监测,核心就在下面这个方法: ```js public JankMonitor(Context context, Reporter reporter) { super(reporter); this.mStrategy = new JankMonitorStrategy(context); this.mReportRows = ((JankMonitorStrategy)this.mStrategy).mReportRows; this.lStuckThreshold = (long)((JankMonitorStrategy)this.mStrategy).lStuckThreshold; this.cStuckThreshold = (long)((JankMonitorStrategy)this.mStrategy).cStuckThreshold; this.criticalBlockTime = (long)((JankMonitorStrategy)this.mStrategy).criticalBlockTime; this.majorBlockTime = (long)((JankMonitorStrategy)this.mStrategy).majorBlockTime; this.bigJankTime = (long)((JankMonitorStrategy)this.mStrategy).bigJankTime; this.samplingFrequency = (long)((JankMonitorStrategy)this.mStrategy).samplingFrequency; this.mHandler = new Handler(handlerThread.getLooper()); if(VERSION.SDK_INT >= 16) { this.mFrameCallback = new FrameCallback() { public void doFrame(long frameTimeNanos) { JankMonitor.this.mSumFrame++; if(JankMonitor.this.mLastFrameTimeNanos != 0L) { long diffMs = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(frameTimeNanos - JankMonitor.this.mLastFrameTimeNanos); if(diffMs >= JankMonitor.this.bigJankTime) { JankMonitor.this.bJank = true; } else if(diffMs >= JankMonitor.this.majorBlockTime) { JankMonitor.this.mMajorBlockCount++; if(diffMs >= JankMonitor.this.criticalBlockTime) { JankMonitor.this.mCriticalBlockCount++; } else if((long)JankMonitor.this.mCriticalBlockCount < JankMonitor.this.cStuckThreshold) { JankMonitor.this.mCriticalBlockCount = 0; } } else if(JankMonitor.this.bJank) { JankMonitor.this.jank("bigJank"); } else if((long)JankMonitor.this.mCriticalBlockCount >= JankMonitor.this.cStuckThreshold) { JankMonitor.this.jank("cStuck"); } else if((long)JankMonitor.this.mMajorBlockCount >= JankMonitor.this.lStuckThreshold) { JankMonitor.this.jank("lStuck"); } else { JankMonitor.this.jank((String)null); } } JankMonitor.this.mLastFrameTimeNanos = frameTimeNanos; Choreographer.getInstance().postFrameCallback(this); } }; } } ```
原创文章,需联系作者,授权转载
上一篇:探索Vue computed 之谜
下一篇:React Router源码分析
相关文章
【技术干货】企业级扫描平台EOS关于JS扫描落地与实践!
京东mPaaS平台之Android组件化系统私有化部署改造实践!
【技术干货】企业级扫描平台EOS-Jenkins集群进阶之路
京东ZERO团队
文章数
39
阅读量
110650
作者其他文章
01
webpack打包组件配置(React版本)
这篇文章是以打包react插件的形式,介绍webpack的一些配置信息。如果写简单插件的话还是推荐使用rollup,但是可以用写插件的形式去学习一下webpack的一些东西。(适用于初中级webpack学者)
01
webpack核心概念与基本实现
webpack 是一个现代 JavaScript 应用程序的静态模块打包器(module bundler)。当 webpack 处理应用程序时,它会递归地构建一个依赖关系图(dependency graph),其中包含应用程序需要的每个模块,然后将所有这些模块打包成一个或多个 bundle。**
01
Typescript合成Webpack中
TypeScript是JavaScript类型的超集,它可以编译成纯JavaScript,简称ts。相对于ES6,TypeScript最大的改善是增加了类型系统,国内外很多大型工程都用它,如AngularJs,白鹭引擎、Antd。
01
小程序加载svg图片
小程序的[组件](https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev/component/)中是没有支持`SVG`标签的。 但是在前端小伙伴的实际开发中,UED经常提供SVG图片过来,如果不想用引入`iconfont`的话,那么妹子我将介绍个很好用的方法。
最新回复
丨
点赞排行
共0条评论
京东ZERO团队
文章数
39
阅读量
110650
作者其他文章
01
webpack打包组件配置(React版本)
01
webpack核心概念与基本实现
01
Typescript合成Webpack中
01
小程序加载svg图片
添加企业微信
获取1V1专业服务
扫码关注
京东云开发者公众号